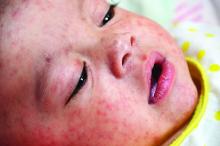
The mother of an 8-month-old calls your office and is hysterical. Her daughter has had cough for a few days with high fevers and now has developed a full body rash. She is worried about measles and is on her way to your office.
We are in the middle of a measles epidemic, there’s no denying it. Measles was declared eliminated in 2000, but reported cases in the United States have been on the rise, and are now at the highest number since 2014. Five months into 2019, there have been 839 reported cases as of May 13). Measles outbreaks (defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as three or more cases) have been reported in California, Georgia, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania. When vaccination rates fall, it is easy for measles to spread. The virus is highly contagious in nonimmune people, because of its airborne spread and its persistence in the environment for hours.
First – is it really measles?
It can be difficult to distinguish the maculopapular rash of measles from similar rashes that occur with more benign viral illnesses. Adding to the challenge, the last major measles outbreak in the United States was over 2 decades ago, and many practicing pediatricians have never seen a single case. So, what clinical features can help distinguish measles from other febrile illnesses?
The prodromal phase of measles lasts approximately 2-4 days and children have high fevers (103°-105° F), anorexia, and malaise. Conjunctivitis, coryza, and cough develop during this phase, and precede any rash. Koplik spots appear during the prodromal phase, but are not seen in all cases. These spots are 1- to 3-mm blue-white lesions on an erythematous base on the buccal mucosa, classically opposite the first molar. The spots often slough once the rash appears. The rash appears 2-4 days after the onset of fever, and is initially maculopapular and blanching. The first lesions appear on the face and neck, and the rash spreads cranial to caudal, typically sparing palms and soles. After days 3-4, the rash will no longer blanch. High fevers persist for 2-4 more days with rash, ongoing respiratory symptoms, conjunctivitis, and pharyngitis. Note that the fever will persist even with development of the rash, unlike in roseola.
It is not only important to diagnosis measles from a public health standpoint, but also because measles can have severe complications, especially in infants and children under 5 years. During the 1989-1991 outbreak, the mortality rate was 2.2 deaths per 1,000 cases (J Infect Dis. 2004 May 1. doi: 10.1086/377694).
Six percent of patients develop pneumonia, which in infants and toddlers can lead to respiratory distress or failure requiring hospitalization. Pneumonia is responsible for 60% of measles deaths, according to the CDC “Pink Book,” Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases, chapter 13 on measles, 13th Ed., 2015. Ocular complications include keratitis and corneal ulceration. Measles also can cause serious neurologic complications. Encephalitis, seen in 1 per 1,000 cases, usually arises several days after the rash and may present with seizure or encephalopathy. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, occurs in approximately 1 per 1,000 cases, typically presents during the recovery phase (1-2 weeks after rash), and can have long-term sequelae. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder, and presents 7-10 years after measles infection.