based on data from a phase 2 randomized trial of individuals with confirmed peanut allergies.
Previous studies have shown that desensitization to peanuts can be successful, but sustained response to oral immunotherapy after treatment reduction or discontinuation has not been well studied, wrote R. Sharon Chinthrajah, MD, of Stanford (Calif.)University, and colleagues.
“We found that OIT with peanut was able to desensitise people with peanut allergy to 4,000 mg of peanut protein, but that discontinuation of peanut, or even a reduction to 300 mg daily, increased the likelihood of regaining clinical reactivity to peanut,” they wrote. “With peanut allergy therapies in varying stages of clinical development, and some nearing [Food and Drug Administration] approval, vital questions remain regarding the durability of treatment effects and the appropriate maintenance doses.”
In the Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Study: Safety Efficacy and Discovery (POISED), published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 120 participants to three groups:
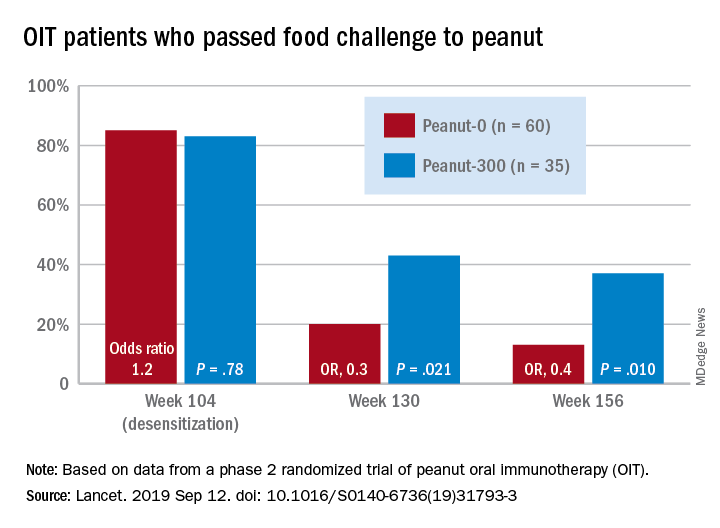
• 60 patients built up to a maintenance dose of 4,000 mg of peanut protein for 104 weeks followed by total discontinuation (peanut-0).
• 35 patients built up to a maintenance dose of 4,000 mg of peanut protein for 104 weeks followed by a 300-mg maintenance dose of peanut protein in the form of peanut flour (peanut-300).
• 25 patients to an oat flour placebo.
All participants were trained on how and when to use epinephrine autoinjector devices to treat allergic symptoms such as respiratory problems (cough, shortness of breath, or change in voice), widespread hives or erythema, repetitive vomiting, persistent abdominal pain, angioedema of the face, or feeling faint.
The primary outcome was passing a double-blind, placebo-controlled, food challenge (DBPCFC) to 4,000 mg of peanut protein, which was measured at baseline and at weeks 104, 117, 130, 143, and 156.
Overall, 35% of the peanut-0 group passed the challenge at 104 and 117 weeks, compared with 4% of the placebo group. At week 156 after discontinuing OIT, 13% of the peanut-0 group met the DBPCFC challenge, compared with 4% of the placebo group. However, 37% of participants randomized to a reduced peanut protein dose of 300 mg passed the challenge at 156 weeks, suggesting that more data are needed on optimal maintenance dosing strategies.
Baseline demographics were similar across all groups. The median age at study enrollment was 11 years and the median allergy duration was 9 years. The most common adverse events were mild gastrointestinal and respiratory problems. Adverse events decreased over time in all three groups.
“Higher levels of peanut-specific IgE to total IgE ratio, peanut sIgE, Ara h 1, Ara h 2, and Ara h 1 IgE to peanut-specific IgE ratio at baseline in participants were associated with increased frequencies of adverse events during active peanut OIT,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the ability of participants to tolerate 4,000 mg of peanut protein after achieving a maintenance dose but conducting serial testing only for those who passed the challenge. In addition, the results may be limited to peanut and not generalizable to other food allergies, the researchers said.
However, the results suggest that OIT remains a promising treatment for peanut allergies, and the association of biomarkers with clinical outcomes “might help the practitioner in identifying good candidates for OIT and those individuals who warrant increased vigilance against allergic reactions during OIT,” they said.
The National Institutes of Health supported the study. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Chinthrajah RS et al. Lancet. 2019 Sep 12. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31793-3.