THE CASE
A 20-year-old man presented to our family medicine clinic with right wrist pain 4 days after falling on his wrist and hand while playing basketball. He denied any other previous injury or trauma. The pain was unchanged since the injury occurred.
Examination demonstrated mild edema over the palmar and ulnar aspect of the patient’s right wrist with no apparent ecchymosis. He had normal range of motion of his right wrist and hand. However, he experienced pain with active and passive wrist extension and ulnar deviation. There was significant tenderness in the palmar and ulnar aspects of his right wrist just distal to the ulnar styloid process.
THE DIAGNOSIS
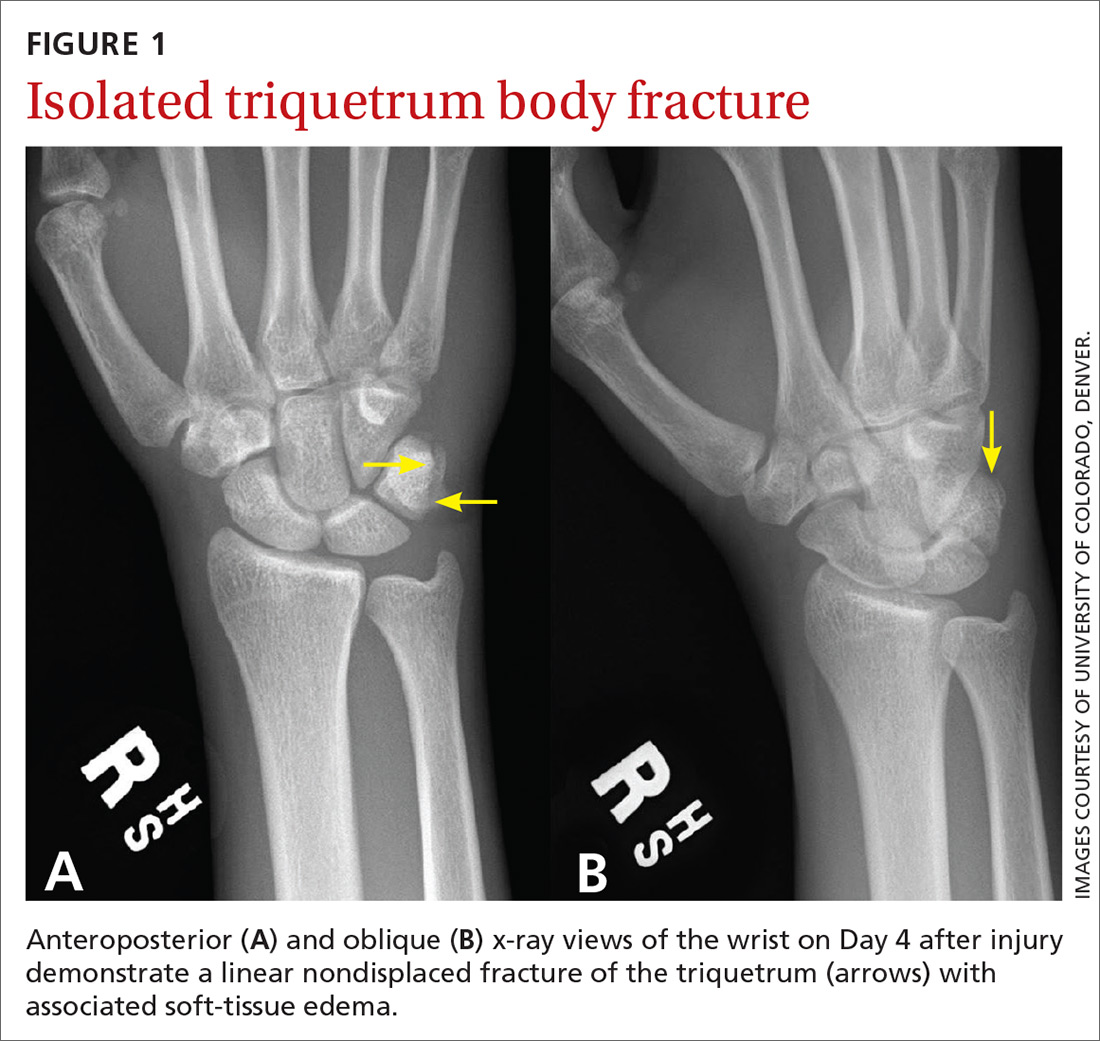
Standard plain x-rays of the right wrist revealed an isolated fracture of the body of the triquetrum (FIGURE 1). Since the patient refused to have a cast placed, his wrist was immobilized with a wrist brace. By Day 16 post injury, the pain and edema had improved significantly. After talking with the patient about the potential risks and benefits of continuing to play basketball—and despite our recommendation that he not play—he decided to continue playing since he was a college basketball prospect.
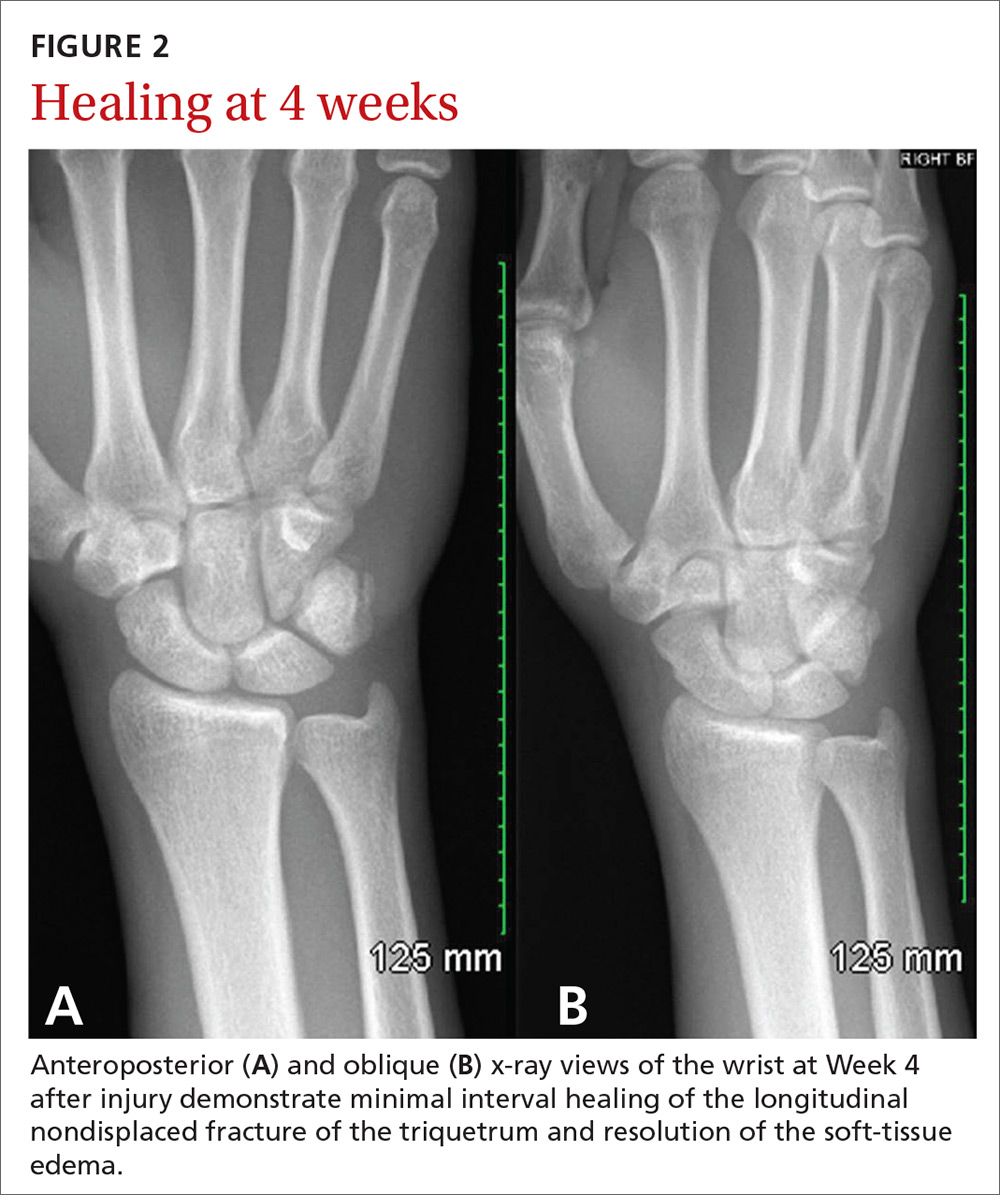
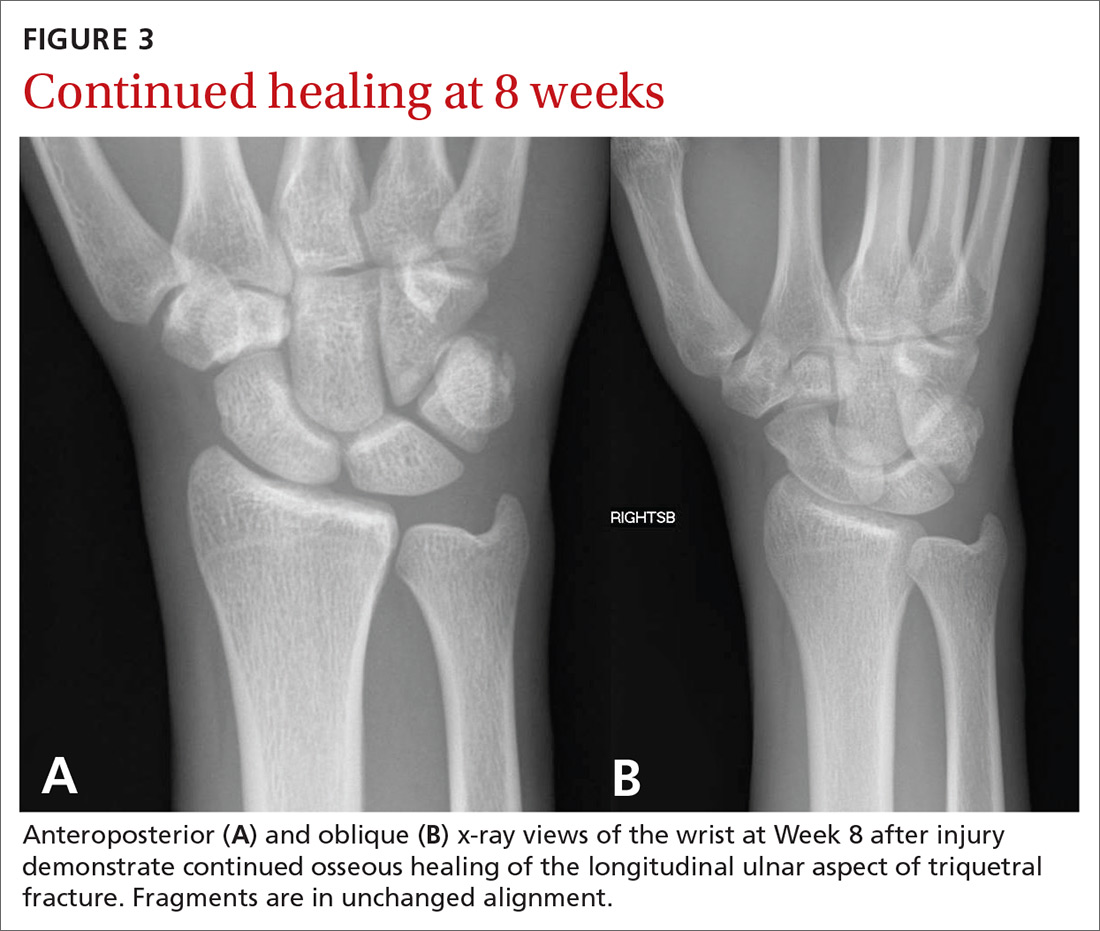
At 4 weeks post injury, x-rays demonstrated mild interval healing (FIGURE 2). At the 8-week visit, the patient had only very mild pain and tenderness, and x-ray images showed improvement (FIGURE 3). Within a few months, his symptoms resolved completely. No further imaging was performed.
DISCUSSION
In general, carpal fractures are uncommon.1 The triquetrum is the second most commonly injured carpal bone, involved in up to 18% of all carpal fractures.2,3 Triquetrum fractures most commonly occur as isolated injuries and are typically classified in 2 general categories: avulsion fractures (dorsal cortex or volar cortex) and fractures of the triquetrum body.4-8 Isolated avulsion fractures of the triquetral dorsal cortex are relatively common, occurring in about 95% of triquetrum injuries.4-9 Isolated fractures of the triquetrum body are less common, occurring in about 4% of triquetrum injuries, and can go unnoticed on conventional x-rays.4-9
Basketball presents a unique risk for hand or wrist fracture due to its high-impact nature, hard playing surfaces, and frequent use of the hands for dribbling, shooting, rebounding, and passing the ball.
In a retrospective study of sports-related fractures conducted at the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, basketball had the highest incidence of carpal injuries compared with other sports, including football, rugby, skiing, snowboarding, and ice-skating.4 Similarly, a retrospective study conducted at the University of California, Los Angeles, found that of all Division 1 collegiate athletes at the school, basketball players had the highest incidence of primary fractures, and the most common fracture location was the hand.10
Continue to: An injury that's easy to miss