Wildfires are on the move in California and communities from the Bay Area to Los Angeles County are once again coping with evacuation, possible destruction of homes, and health concerns related to poor air quality and smoke.
What can doctors tell their patients with cardiovascular and pulmonary conditions about the risks of smoke from wildfires?
EPA resources online
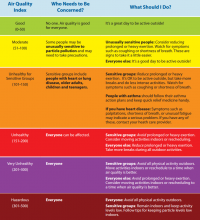
AirNow, a website managed by the Environmental Protection Agency, provides a variety of resources for the public and for health providers, including links to online tutorials, printable health fact sheets, and the newly updated document “Wildfire Smoke: Guide for Public Health Officials 2019.” When wildfire smoke generates an Air Quality Index (AQI) from 101-150, at-risk subgroups like people with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or heart disease should take precautions.
“An AQI of 151-200 is unhealthy for everyone, and an AQI above 200 is very unhealthy,” John R. Balmes, MD, a pulmonologist at the University of California, San Francisco, and an expert on the respiratory and cardiovascular effects of air pollutants, said in an interview. “That does not mean that everybody is going to die, though. You’re going to have some symptoms of scratchy throat, and you may cough once or twice an hour [from exposure to wildfire smoke], but people who don’t have any preexisting health problems are probably going to be fine and don’t necessarily have to wear an N95 mask. People should wear one if they need to feel comfortable.”