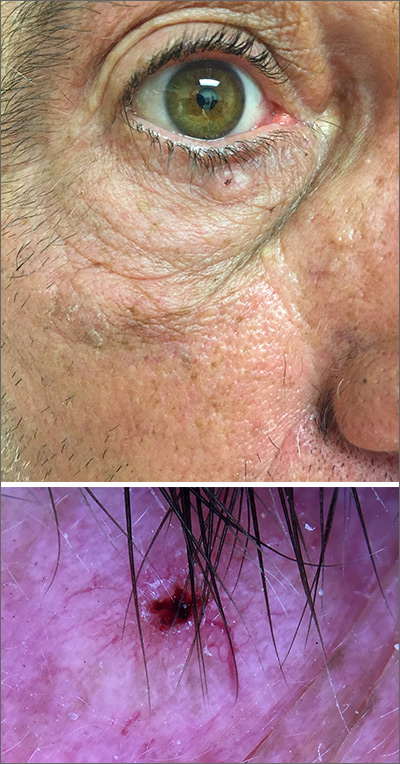
While the lesion’s proximity to the eyelashes and lid margin made dermoscopy difficult, the physician was able to use a dermatoscope to view the lesion and recognize it as nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). (If dermoscopy had not been an option, a hand magnifier or otoscope could have been used to help with magnification and diagnosis.)
Nodular BCCs usually present with a raised pearly border, a central ulceration, and telangiectasias. In this case, the central erosion was much more obvious with dermoscopy. Also visible were abnormal telangiectasias around the central erosion; they were especially dilated and tortuous (referred to as an arborizing pattern) at the 4:00 position. The diagnosis was confirmed by a small tangential shave biopsy of the inferior aspect of the lesion.
BCCs are referred for Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) when they are any of the following: in high-risk locations such as the T-zone of the face (eyes, nose, and mouth); > 2 cm in diameter; a recurrence of a previous BCC; or a high-risk type including infiltrating, morpheaform, or basosquamous (based on pathology). Lower risk nodular BCCs are usually treated with excision or electrodesiccation and curettage.
In this case, the BCC was in a high-risk location and required MMS. The challenge was that the lesion was so close to the lid margin that resection of the cancer and subsequent repair could lead to ectropion/poor lid closure. The Mohs surgeon resected the lesion in 3 stages. The oculoplastic surgeon then closed the defect via a multilayered repair.
Images and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.