Molar pregnancy is an uncommon but serious condition that affects young women of reproductive age. The diagnosis and management of molar pregnancy is familiar to most gynecologists. However, in the days and weeks following evacuation of molar pregnancy, clinicians face a critical time period in which they must be vigilant for the development of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). If recognized early and treated appropriately, it almost always can be cured; however, errors or delays in the management of this condition can have catastrophic consequences for patients, including decreasing the likelihood of cure. Here we will review some of the steps and actions that can be taken immediately following the diagnosis of a molar pregnancy to expeditiously identify postmolar GTN and ensure patients are appropriately prepared for further consultation and intervention.
Postmolar GTN includes the diagnoses of invasive mole and choriocarcinoma that contain highly atypical trophoblasts with the capacity for local invasion and metastasis. Typically, the diagnosis is made clinically and not distinguished with histology. While molar pregnancies are a benign condition, invasive moles and choriocarcinoma are malignant conditions in which the molar tissue infiltrates the uterine myometrium, vasculature, and frequently is associated with hematogenous spread with distant metastases. It is a highly chemosensitive disease, and cure with chemotherapy typically is achieved with the ability to preserve fertility if desired even in advanced stage disease.1
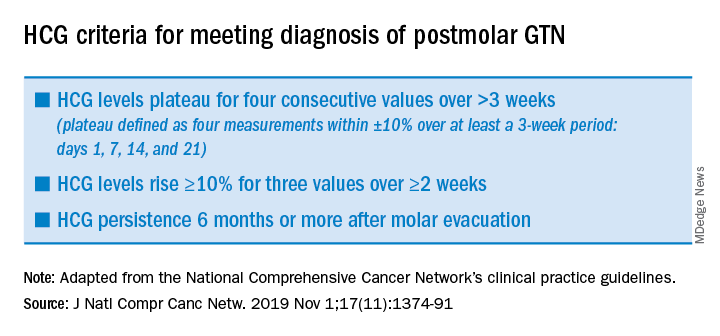
After evacuation of a molar pregnancy, gynecologists should be on alert for the development of postmolar GTN if the following known risk factors are present: a history of a prior GTN diagnosis, complete mole on pathology (as opposed to partial mole), serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels greater than 100,000 mIU/mL, age greater than 40 years, an enlarged uterus or large ovarian theca lutein cysts, and slow to normalize (more than 2 months) hCG. Symptoms for the development of postmolar GTN include persistent vaginal bleeding after evacuation, a persistently enlarged or enlarging uterine size, and adnexal masses. Ultimately, the diagnosis is made through plateaued or rising serum hCG assessments.2 (See graphic.)
Following the evacuation of a molar pregnancy, hCG levels should be drawn at the same laboratory every 1-2 weeks until normalization and then three consecutive normal values. Once this has been achieved, hCG levels should be tested once at 3 months and again at 6 months. During this 6 month period, patients should use reliable contraception, ideally, and through oral contraceptive pills that suppress the secretion of pituitary hCG if not contraindicated. Should a woman become pregnant during this 6-month surveillance, it becomes impossible to rule out occult postmolar GTN.
Typically after evacuation of a molar pregnancy, there is rapid fall in hCG levels, but this does not occur when the molar pregnancy has become invasive or is associated with choriocarcinoma. In these cases, after an initial drop in hCG levels, there is an observed rise or plateau in levels (as defined in the accompanying table), and this establishes the diagnosis of postmolar GTN. It is common for hCG to fall in fits and starts, rather than have a smooth, consistent diminution, and this can be worrying for gynecologists; however, provided there is a consistent reduction in values in accordance with the stated definitions, observation can continue.
Another source of confusion and concern is an HCG level that fails to completely normalize during observation, yet reaches a very low level. If this is observed, clinicians should consider the diagnosis of quiescent hCG, pituitary hCG, or phantom hCG.3 These can be difficult to distinguish from postmolar GTN, and consultation with a gynecologic oncologist with experience in the diagnosis and management of these rare tumors is helpful to determine if the persistent low levels in hCG require intervention.
Once a clinician has observed a plateau or rise in hCG levels, a gynecologic examination should be performed because the lower genital tract is a common site for metastatic postmolar GTN. If during this evaluation, a suspicious lesion is identified (typically a blue-black, slightly raised, hemorrhagic-appearing lesion), it should not be biopsied, but rather assumed to be a metastatic site. The vasculature of metastatic sites is extremely fragile, and biopsy or disruption can result in catastrophic hemorrhage, even from very small lesions.
In addition to physical examination, several diagnostic studies should be performed which may expedite the triage and management of the case. A pelvic ultrasound should evaluate the endometrial cavity for a new viable pregnancy, and residual molar tissue; sometimes, myometrial invasion consistent with an invasive mole can be appreciated. Chest x-ray or CT scan should be ordered to evaluate for pulmonary metastatic lesions. Additionally, CT scans of the abdomen and pelvis should be ordered, and if lung metastases are present, brain imaging with either MRI or CT scan also should be obtained. These imaging studies will provide the necessary information to stage the GTN (as metastatic or not).
Treatment for postmolar GTN is determined based on further prognostic categorization (“high risk” or “low risk”) in accordance with the WHO classification, which is derived using several prognostic clinical variables including age, antecedent pregnancy, interval from index pregnancy, pretreatment hCG, largest tumor size, sites and number of metastases, and response to previous chemotherapy.4 These assignments are necessary to determine whether single-agent or multiagent chemotherapy should be prescribed.
Laboratory studies are helpful to obtain at this time and include metabolic panels (which can ensure that renal and hepatic function are within normal limits in anticipation of future chemotherapy), and complete blood count ,which can establish viable bone marrow function prior to chemotherapy.
Once postmolar GTN has been diagnosed, it is most appropriate to refer the patient to a gynecologic oncologist with experience in the treatment of these relatively rare malignancies. At that point, the patient will be formally staged, and offered treatment based on these staging results.
Among women with low-risk, nonmetastatic GTN who desire future fertility it is appropriate to offer a repeat dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure rather than immediately proceeding with chemotherapy. Approximately two-thirds of women with low risk disease can avoid chemotherapy with repeat curettage.5 Risk factors for needing chemotherapy after repeat D&C include the presence of trophoblastic disease in the pathology specimen and urinary hCG levels greater than 1,500 mIU/mL at the time of curettage. In my experience, many women appreciate this option to potentially avoid toxic chemotherapy.
For women with low-risk, nonmetastatic postmolar GTN who do not desire future fertility, and hope to avoid chemotherapy, hysterectomy also is a reasonable first option. This can be performed via either minimally invasive, laparotomy, or vaginal route. If performing a minimally invasive procedure in the setting of GTN, there should be caution or avoidance of use of a uterine manipulator because the uterine wall typically is soft and prone to perforation, and bleeding can be significant secondary to disruption of the tumor.
If repeat D&C or hysterectomy are adopted instead of chemotherapy, it is important that patients are very closely monitored post operatively to ensure normalization of their hCG levels (as described above). If it fails to normalize, restaging scans and examinations should be performed, and referral for the appropriate chemotherapy regimen should be initiated without delay.
Postmolar GTN is a serious condition that usually can be cured with chemotherapy or, if appropriate, surgery. and refer to a gynecologic oncologist when criteria are met to ensure that overtreatment is avoided and essential therapy is ensured.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Lancet Oncol. 2007 Aug;8(8):715-24.
2. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019 Nov 1;17(11):1374-91.
3. Gynecol Oncol. 2009 Mar;112(3):663-72.