Nationally, an estimated 5.7% of all outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Jan. 25, which was up from 5.1% the previous week but still lower than the current seasonal high of 7.1% recorded during the week of Dec. 22-28, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Another key indicator of influenza activity, the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also remains high as it rose from 25.7% the week before to 27.7% for the week ending Jan. 25, the influenza division said. That is the highest rate of the 2019-2020 season so far, surpassing the 26.8% reached during Dec. 22-28.
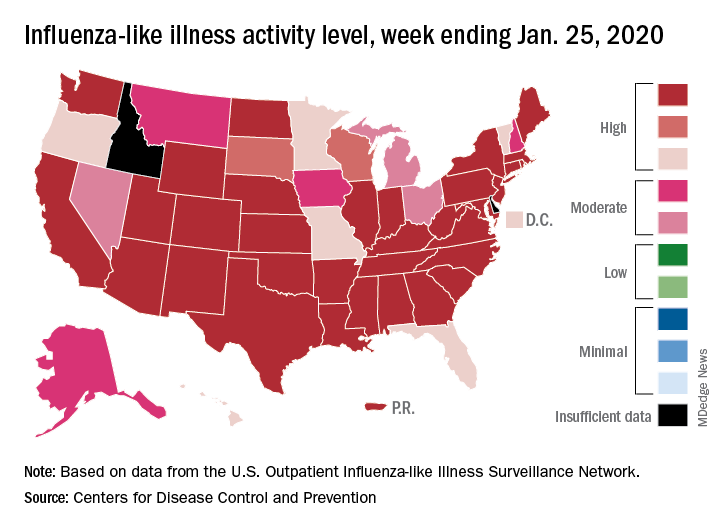
Another new seasonal high involves the number of states, 33 plus Puerto Rico, at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the latest reporting week, topping the 32 jurisdictions from the last full week of December. Another eight states and the District of Columbia were in the “high” range with activity levels of 8 and 9, and no state with available data was lower than level 6, the CDC data show.
Going along with the recent 2-week increase in activity is a large increase in the number of ILI-related pediatric deaths, which rose from 39 on Jan. 11 to the current count of 68, the CDC said. At the same point last year, there had been 36 pediatric deaths.
Other indicators of ILI severity, however, “are not high at this point in the season,” the influenza division noted. “Overall, hospitalization rates remain similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons, but rates among children and young adults are higher at this time than in recent seasons.” Overall pneumonia and influenza mortality is also low, the CDC added.