according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases reported up to that date was 442,785, or 9.3% of the total COVID-19 case load of more than 4.76 million among all ages. There have been only 92 pediatric deaths, however, which works out to just 0.06% of the 154,279 reported for all ages, the AAP and the CHA said Aug. 24 in their most recent update.
Child hospitalizations also were on the low side, representing 1.7% (4,062) of the cumulative total of 234,810 admissions among all ages as of Aug. 20, based on data from 21 states and New York City.
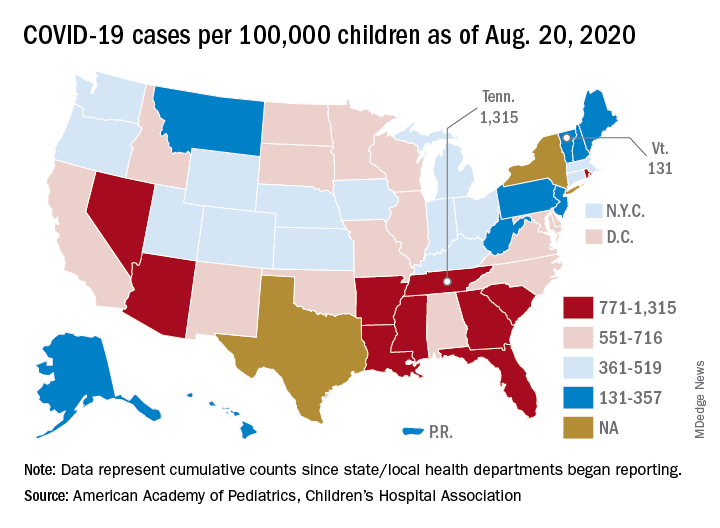
Nationally, the cumulative number of reported child cases is now up to 583 per 100,000 children, and that figure covers 49 states, Washington, D.C., Guam, New York City, and Puerto Rico.
There is some disagreement among the states, though, about the definition of “child.” Most states use an age range of 0-17, 0-18, or 0-19, but Florida and Utah go with a range of 0-14 years while South Carolina and Tennessee consider humans aged 0-20 years to be children. Other data limitations involve Texas, which has reported age distribution for only 8% of all cases, and New York, which is not reporting the age distribution of statewide cases, the AAP/CHA report noted.
The definition of child isn’t the only thing that varies between the states. The cumulative case rate for Tennessee, the highest in the country at 1,315 per 100,000 children, is 10 times that of Vermont, which is the lowest at 131 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA said. Vermont reports child COVID-19 cases using an age range of 0-19 years.
The other states with rates over 1,000 cases per 100,000 children are Arizona (1,300), which had the highest rate a week ago; South Carolina (1,214); Louisiana (1,127); Mississippi (1,120); and Nevada (1,068). Those with rates below 200 cases per 100,000 children are Maine (150), New Hampshire (175), and Hawaii (188), according to this week’s report.