according to an analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
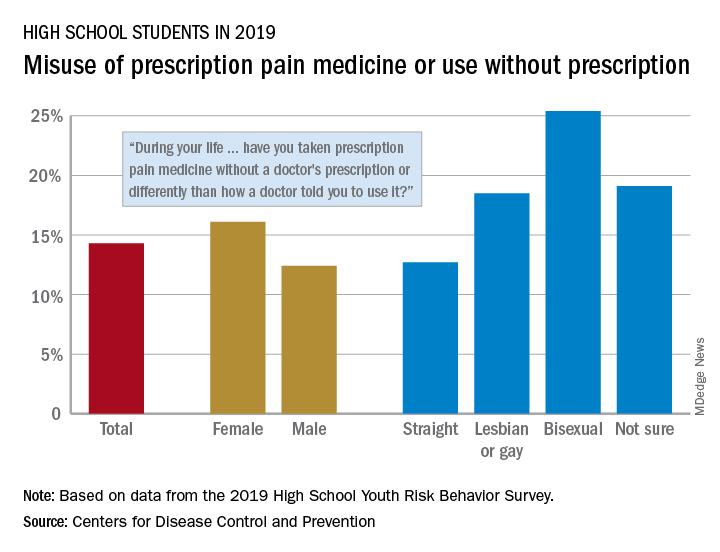
That type of opioid use/misuse, reported by 14.3% of respondents to the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, was more common among females (16.1%) than males (12.4%) and even more prevalent among nonheterosexuals and those who are unsure about their sexual identity, Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The YRBS data show that 18.5% of gay or lesbian students had, at some point in their lives, used a prescription opioid differently than a physician had told them to or taken one without a prescription. That figure was slightly higher (19.1%) for those unsure of their sexual identity, considerably higher (25.4%) for bisexuals, and lower for heterosexuals (12.7%), they reported.
The pattern for current use/misuse of opioids, defined as use one or more times in the 30 days before the survey, was similar to ever use but somewhat less pronounced in 2019. Prevalence was 7.2% for all students in grades 9-12, 8.3% for females, and 6.1% for males. By sexual identity, prevalence was 6.4% for heterosexuals, 7.6% for gays or lesbians, 11.5% for those unsure about their sexual identity, and 13.1% for bisexuals, based on the YRBS data.
This increased misuse of opioids among sexual minority youths, “even after controlling for other demographic and substance use characteristics ... emphasizes the importance of identifying tailored prevention strategies to address disparities among this vulnerable population,” the CDC researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Jones CM et al. MMWR Suppl. 2020 Aug 21;69(1):38-46.