The number of new cases soared in the past week as the United States exceeded 1 million children infected with the coronavirus, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
For the first time, the number of cases in children for the week ending Nov. 12 passed 100,000, and it didn’t stop until it reached 111,946, bringing the total for the pandemic to 1,039,464 reported cases in 49 states (New York is not reporting ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, and Guam, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 update.
“As a pediatrician who has practiced medicine for over 3 decades, I find this number staggering and tragic. We haven’t seen a virus flash through our communities in this way since before we had vaccines for measles and polio,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
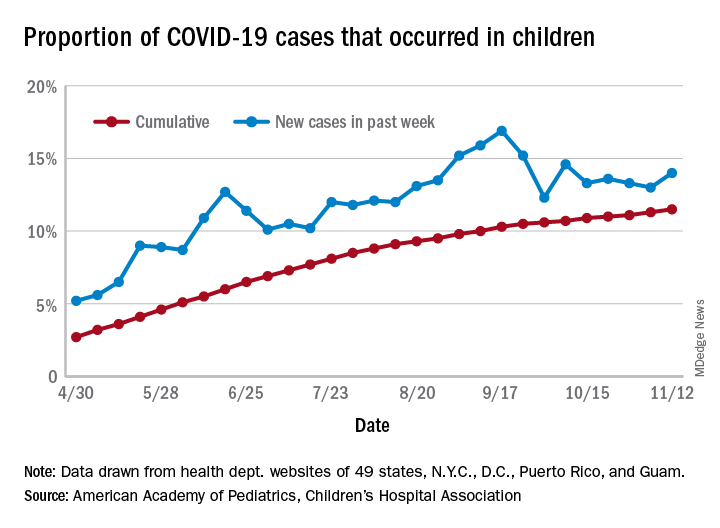
The previous 1-week high of almost 74,000 cases came just last week, and that number had surpassed the previous week’s new high of 61,000. The number of cumulative child cases, meanwhile, has doubled since Sept. 3, when it was just over 513,000. Children now represent 11.5% of all COVID-19 cases since the start of the pandemic in the jurisdictions reporting age distribution, the AAP and CHA said.
For the week ending Nov. 12, COVID-19 cases children made up 14% of cases nationally, rising from 13% the week before and reversing a decline that started in mid-October, the AAP/CHA data show.
The two groups continue to note the rarity of severe illness in children, but the number of deaths nationally had its biggest 1-week increase since late July, as the total rose from 123 to 133 in the 42 states reporting such data by age, as well as New York City. The cumulative hospitalization rate for children decreased slightly in the past week and is now down to 1.6% in the 23 states (and NYC) with available data, the AAP and CHA said.
The AAP called on elected leaders to enact a national strategy to combat the spread of the virus and urged health authorities to do more to collect data on longer-term impacts on children.
We’re very concerned about how this will impact all children, including toddlers who are missing key educational opportunities, as well as adolescents who may be at higher risk for anxiety and depression,” Dr. Goza said.