New analysis of data from studies 302 and 4000
Both studies were carried out in adults with advanced illness and OIC whose conditions were refractory to laxative use. Both of the studies were placebo controlled.
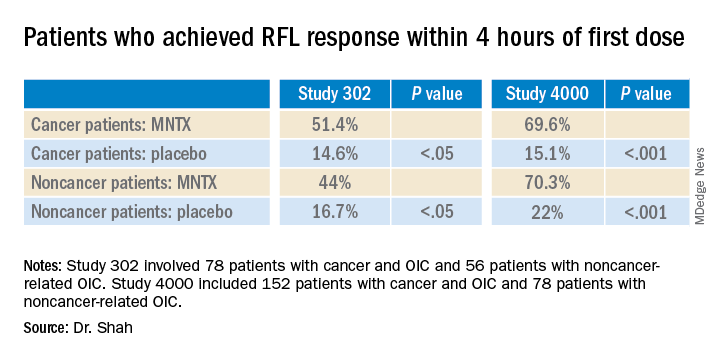
Study 302 involved 78 patients with cancer and 56 patients with noncancer-related OIC. MNTX was given at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg subcutaneously every other day for 2 weeks.
Study 4000 included 152 patients with cancer and OIC and 78 patients with noncancer-related OIC. In this study, the dose of MNTX was based on body weight. Seven or fewer doses of either 8 mg or 12 mg were given subcutaneously for 2 weeks.
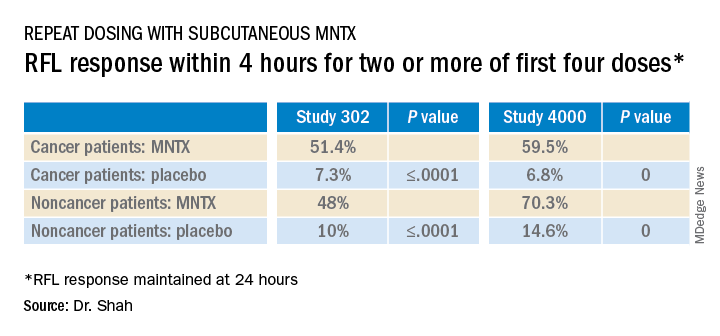
The main endpoints of both studies was the proportion of patients who achieved a rescue-free laxation (RFL) response within 4 hours after the first dose and the proportion of patients with an RFL response within 4 hours for two or more of the first four doses within 24 hours.
Dr. Shah explained that RFL is a meaningful clinical endpoint. Patients could achieve a bowel movement with the two prespecified time endpoints in both studies.
Not all patients were hospitalized for OIC, Dr. Shah noted. Entry criteria were strict and included having fewer than three bowel movements during the previous week and no clinically significant laxation (defecation) within 48 hours of receiving the first dose of study drug.
“In both studies, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with MNTX versus placebo achieved an RFL within 4 hours after the first dose among both cancer and noncancer patients,” the investigators reported.
Results were relatively comparable between cancer and noncancer patients who were treated for OIC in study 4000, the investigators noted.
Both studies were sponsored by Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shah has received travel fees from Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Brenner has served as a consultant for Salix Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Purdue Pharma. AstraZeneca developed naloxegol.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.