Second, the physician serves an important role in directing and coordinating the team of professionals involved. This primarily means helping the team to communicate with one another. Before home visits begin, the physician’s office should reach out not only to the patient and family, but also to any other health care personnel involved in the patient’s home care. Otherwise, many of the health care providers involved will never have face-to-face interaction with the physician. Creation of the coordinated health team minimizes duplication and miscommunication; it also builds a valuable bond.
How does one go about making a home visit?
Scheduling. What often works best in a busy practice is to schedule home visits for the end of the workday or to devote an entire afternoon to making home visits to several patients in one locale. Also important is scheduling times, if possible, when important family members or other caregivers are at home or when other members of the home care team can accompany you.
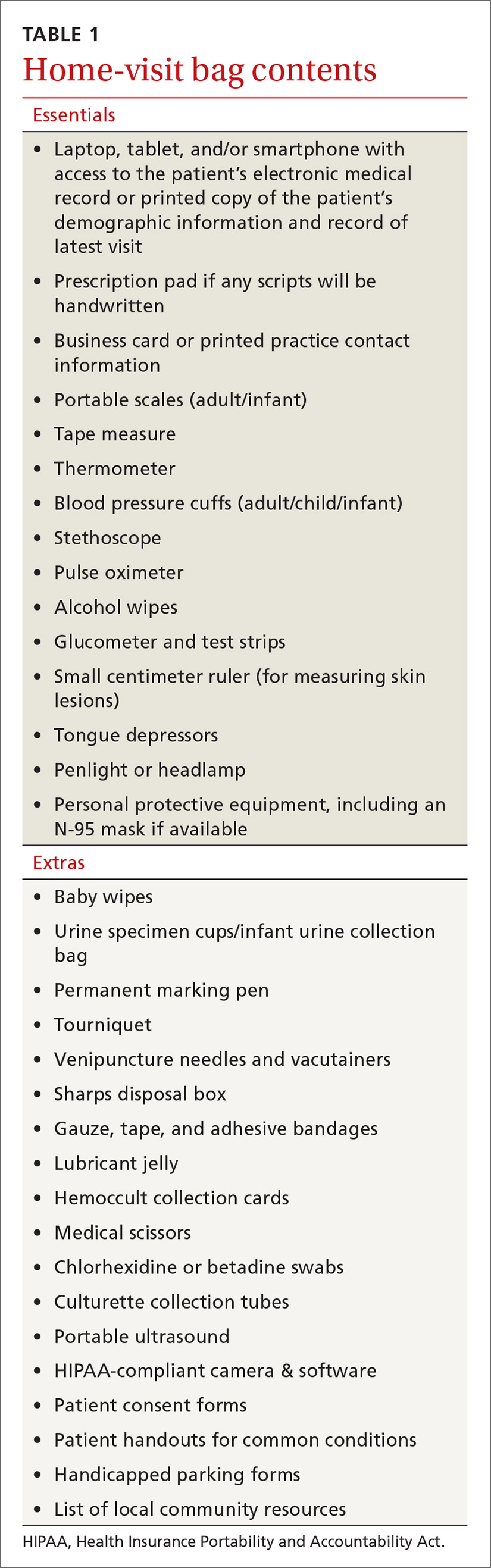
What to bring along. Carry a “home visit bag” that includes equipment you’re likely to need and that is not available away from your office. A minimally equipped visit bag would include different-sized blood pressure cuffs, a glucometer, a pulse oximeter, thermometers, and patient education materials. Other suggested contents are listed in TABLE 1. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, providers should also carry adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), including an N-95 mask.
Dos and don’ts. Take a few minutes when you first arrive to simply visit with the patient. Sit down and introduce yourself and any members of the home care team that the patient has not met. Take an interim history. While you’re doing this, be observant: Is the home neat or cluttered? Is the indoor temperature comfortable? Are there fall hazards? Is there a smell of cigarette smoke? Are there any indoor combustion sources (eg, wood stove or kerosene heater)? Ask questions such as: Who lives here with you? Can you show me where you keep your medicines? (If the patient keeps insulin or any other medicines in the refrigerator, ask to see it. Note any apparent food scarcity.)
During your exam, pay particular attention to whether vital signs are appreciably different than those measured in the office or hospital. Pay special attention to the patient’s functional abilities. “A subtle, but critical distinction between medical management in the home and medical management in the hospital, clinic, or office is the emphasis on the patient’s functional abilities, family assistance, and environmental factors.”33
Observe the patient’s use of any home technology, if possible; this can be as simple as home oxygenation or as complex as home hemodialysis. Assess for any apparent caregiver stress. Finally, don’t neglect to offer appropriate emotional and spiritual support to the patient and family and to schedule the next follow-up visit before you leave.
Continue to: Documentation and reimbursement.