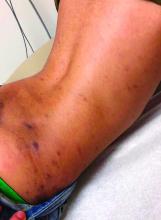
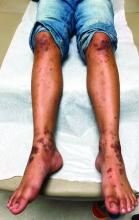
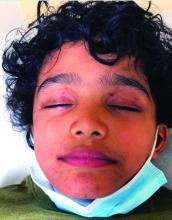
Because of the lack of improvement with topical corticosteroids, a skin biopsy was performed from a lesion on the lower back which showed an epidermis with compact hyperkeratosis and a thickened granular layer. Within the dermis, there was a lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes with a prominent interface change and rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes consistent with lichen planus.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition of the skin seen mainly in the adult population and is rare in children. This condition affects 0.5%-1% of the population, with maybe a higher prevalence in woman with no racial predilection in the adult or pediatric population. Most patients diagnosed are described to be over 40 years of age, but in children, the mean age for presentation is reported between the ages of 7 and 11.8 years.1 Interestingly, most of the published larger studies of lichen planus in children originate from India. In a U.K. study, about 80% of the cases reported were from children of Indian descent, as is our patient; so it is possible that lichen planus may be more prevalent in India.1 In a study based in the United States, cases were more prevalent in African American children.2
The exact cause of this condition is not known but studies have suggested that activated T cells, particularly CD8+, attack and cause apoptosis of the basal keratinocytes.3 There appears to be an up-regulation of Th1 cytokines such as interferon‐gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, interleukin‐1 alpha, IL‐6, and IL‐8, as well as other apoptosis-related molecules.3
Lichen planus has been associated with other systemic conditions especially liver disease (chronic active hepatitis C and primary biliary cirrhosis). Children and adults may also have coexistence of other autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, myasthenia gravis, autoimmune thyroid disease, vitiligo, and thymoma. Some reports have also found a higher prevalence of atopic dermatitis in children with lichen planus.4
The lesions are typically described as the four “Ps” for pruritic, polygonal, purpuric flat-topped papules, and plaques. The papules of lichen planus have characteristically dry fine white streaks known as Wickham’s striae. The lesions can occur anywhere on the body, but they tend to occur more commonly on the flexures of the forearms, the wrists, ankles, shins, knees, and the torso. The face is rarely affected. In some patients oral, scalp (lichen planopilaris), nails, and rarely conjunctival, genital, and esophageal involvement can occur.2
In histopathology, the lesions are characterized by a wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, marked hyperkeratosis, and irregular sawtooth-like acanthosis of rete ridges on the epidermis. The dermal-epidermal junction typically shows an interstitial dermatitis. Civatte bodies may also be seen. On direct immunofluorescence, IgM-staining of the cytoid bodies in the dermal papilla or peribasilar areas are suggestive of lichen planus.1
The differential diagnosis of lichen planus includes severe lichenified atopic dermatitis, drug-induced lichen planus, graft-versus-host disease, psoriasis, pityriasis rosea, subacute cutaneous lupus, discoid lupus, secondary syphilis, and lichen simplex chronicus. Interestingly, our patient presented with lesions that were not pruritic and more generalized. Compared with eczema, were flexures are commonly affected, our patient’s lesions were localized to the ankles, wrists, extensor knees, and elbows, and no pruritus was reported. Lichenification of skin lesions occurs as a response to chronic scratching as it occurs in atopic dermatitis and lichen simplex chronicus, was considered in our patient, but the lack of pruritus and the more acute presentation made it unlikely.
Lichen planus is considered a self-limiting disease, so treatment is focused on the control of pruritus and to accelerate resolution. The first-line therapy for classic cutaneous lichen planus is the use of potent or superpotent topical corticosteroids for localized disease on the body and extremities and mild to mid-potency for intertriginous areas and the face. Clinical response should be assessed after 2-3 weeks of treatment. For patients with more generalized or recalcitrant disease like our patient, other treatment modalities like phototherapy (narrow-band UVB), a 4- to 6-week course of oral glucocorticoids, or acitretin may be considered. Our patient recently started narrow-band UVB. Other medications that have been reported beneficial for more severe cases include methotrexate, cyclosporine, griseofulvin, hydroxychloroquine, metronidazole, dapsone, and mycophenolate. Recent studies in the adult population have shown apremilast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, to be a promising medication for patients with cutaneous lichen planus, though this medication has not been approved yet for use in the pediatric population.5
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Payette MJ et al. Clin Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;33(6):631-43.
2. Walton KE et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:34-8.
3. Lehman JS et al. Int J Dermatol. 2009 Jul;48(7):682-94.
4. Laughter D et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:649-55.
5. Paul J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Feb;68(2):255-61.