Exercise training – but not testosterone therapy – improved vascular health in aging men with widening midsections and low to normal testosterone, new research suggests.
“Previous studies have suggested that men with higher levels of testosterone, who were more physically active, might have better health outcomes,” Bu Beng Yeap, MBBS, PhD, University of Western Australia, Perth, said in an interview. “We formulated the hypothesis that the combination of testosterone treatment and exercise training would improve the health of arteries more than either alone.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators randomly assigned 80 men, aged 50-70 years, to 12 weeks of 5% testosterone cream 2 mL applied daily or placebo plus a supervised exercise program that included machine-based resistance and aerobic (cycling) exercises two to three times a week or no additional exercise.
The men (mean age, 59 years) had low-normal testosterone (6-14 nmol/L), a waist circumference of at least 95 cm (37.4 inches), and no known cardiovascular disease (CVD), type 1 diabetes, or other clinically significant illnesses. Current smokers and men on testosterone or medications that would alter testosterone levels were also excluded.
High-resolution ultrasound of the brachial artery was used to assess flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and sublingual glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) responses. FMD has been shown to be predictive of CVD risk, with a 1% increase in FMD associated with a 9%-13% decrease in future CVD events.
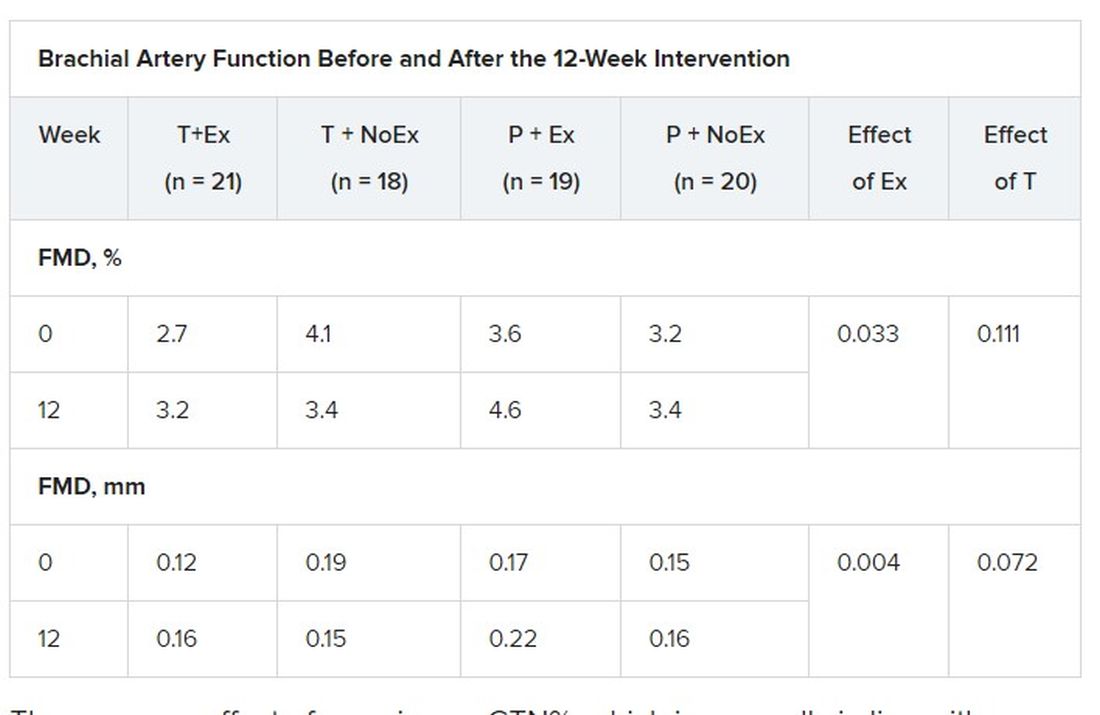
Based on participants’ daily dairies, testosterone adherence was 97.6%. Exercise adherence was 96.5% for twice-weekly attendance and 80.0% for thrice-weekly attendance, with no between-group differences.
As reported Feb. 22, 2021, in Hypertension, testosterone levels increased, on average, 3.0 nmol/L in both testosterone groups by week 12 (P = .003). In all, 62% of these men had levels of the hormone exceeding 14 nmol/L, compared with 29% of those receiving placebo.
Testosterone levels improved with exercise training plus placebo by 0.9 nmol/L, but fell with no exercise and placebo by 0.9 nmol/L.
In terms of vascular function, exercise training increased FMD when expressed as both the delta change (mm; P = .004) and relative rise from baseline diameter (%; P = .033).
There was no effect of exercise on GTN%, which is generally in line with exercise literature indicating that shear-mediated adaptations in response to episodic exercise occur largely in endothelial cells, the authors noted.
Testosterone did not affect any measures of FMD nor was there an effect on GTN response, despite previous evidence that lower testosterone doses might enhance smooth muscle function.
“Our main finding was that testosterone – at this dose over this duration of treatment – did not have a beneficial effect on artery health, nor did it enhance the effect of exercise,” said Dr. Yeap, who is also president of the Endocrine Society of Australia. “For middle-aged and older men wanting to improve the health of their arteries, exercise is better than testosterone!”
Shalender Bhasin, MBBS, director of research programs in men’s health, aging, and metabolism at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said the study is interesting from a mechanistic perspective and adds to the overall body of evidence on how testosterone affects performance, but was narrowly focused.
“They looked at very specific markers and what they’re showing is that this is not the mechanism by which testosterone improves performance,” he said. “That may be so, but it doesn’t negate the finding that testosterone improves endurance and has other vascular effects: it increases capillarity, increases blood flow to the tissues, and improves myocardial function.”
Although well done, the study doesn’t get at the larger question of whether testosterone increases cardiovascular risk, observed Dr. Bhasin. “None of the randomized studies have been large enough or long enough to determine the effect on cardiovascular events rates. There’s a lot of argument on both sides but we need some data to address that.”
The 6,000-patient TRAVERSE trial is specifically looking at long-term major cardiovascular events with topical testosterone, compared with placebo, in hypogonadal men aged 45-80 years age who have evidence of or are at increased risk for CVD. The study, which is set to be completed in April 2022, should also provide information on fracture risk in these men, said Dr. Bhasin, one of the trial’s principal investigators and lead author of the Endocrine Society’s 2018 clinical practice guideline on testosterone therapy for hypogonadism in men.
William Evans, MD, adjunct professor of human nutrition, University of California, Berkley, said in an interview that the positive effects of testosterone occur at much lower doses in men and women who are hypogonadal but, in this particular population, exercise is the key and the major recommendation.
“Testosterone has been overprescribed and overadvertised for essentially a lifetime of sedentary living, and it’s advertised as a way to get all that back without having to work for it,” he said. “Exercise has a profound and positive effect on control of blood pressure, function, and strength, and testosterone may only affect in people who are sick, people who have really low levels.”
The study was funded by the Heart Foundation of Australia. Lawley Pharmaceuticals provided the study medication and placebo. Dr. Yeap has received speaker honoraria and conference support from Bayer, Eli Lilly, and Besins Healthcare; research support from Bayer, Lily, and Lawley; and served as an adviser for Lily, Besins Healthcare, Ferring, and Lawley. Dr. Shalender reports consultation or advisement for GTx, Pfizer, and TAP; grant or other research support from Solvay and GlaxoSmithKline; and honoraria from Solvay and Auxilium. Dr. Evans reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.