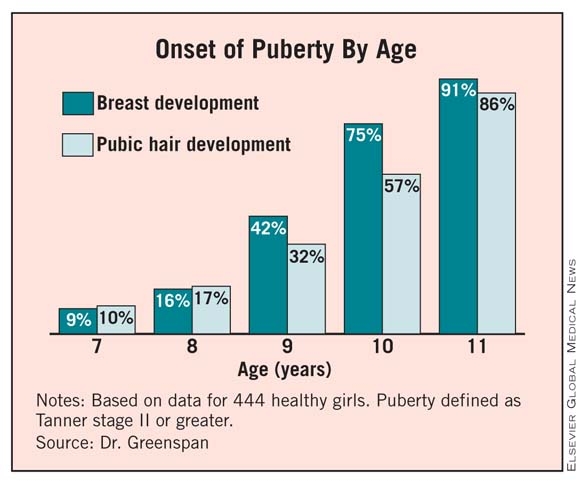
DENVER – A majority of girls start puberty before age 10 years, according to researchers for a longitudinal study who found young ages for onset of breast and pubic hair development.
Tanner stage II breast development ranged from 9% of 7-year-old girls to 91% of 11-year-olds in this ongoing study of 444 healthy girls. Similarly, 10% of the 7-year-olds had Tanner stage II pubic hair development, as did 86% of the 11-year-olds. A total of 75% achieved Tanner stage II or greater breast development, and 57% achieved Tanner stage II or greater pubic hair development by age 10 years.
"Observations from this longitudinal cohort study confirm that girls’ pubertal development is starting earlier," Dr. Louise C. Greenspan said at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies, where she presented data for the first 5 years. Data from the first 2 years were previously published (Pediatrics 2010;126:e583-90).
A higher body mass index (BMI) and black ethnicity were associated with earlier onset of puberty, said Dr. Greenspan, a pediatric endocrinologist at the Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Medical Center. Girls were aged 6-8 years in 2005 or 2006 when they were initially enrolled in the Cohort Study of Young Girls’ Nutrition, Environment, and Transitions (CYGNET). Participants are 42% white, 24% Hispanic, 22% black, and 12% Asian, "a historically understudied group in this field."
"When we break this down by ethnicity ... not surprisingly, the black girls were earlier for all stages of breast development," Dr. Greenspan said, whereas white girls were the later bloomers at all stages of breast development.
The black girls also were earlier for all stages of pubic hair development. By age 11 years, for example, almost 98% were at Tanner stage II or higher. "The difference here is that the Asian girls were the later girls, basically all the way along, for pubic hair development," Dr. Greenspan said.
Girls who were below the 85th percentile for BMI were the later bloomers at all stages of pubertal development, Dr. Greenspan said. She added that when girls had a high body-fat percentage on bioelectrical impedance analysis, examiners palpated them to try to distinguish fat from glandular tissue. In a similar fashion, the slimmer girls were the later developers of pubic hair at Tanner stage II.
Breast-development findings in the current study are similar to those reported by investigators for American Academy of Pediatrics’ Pediatric Research in Office Settings (PROS) research network.
"For breast stage, there were some variations, but it was pretty much on par," Dr. Greenspan said. However, for pubic hair, CYGNET participants had earlier rates of development versus those in the PROS cross-sectional study (Pediatrics 1997;99:505-12).
A meeting attendee asked Dr. Greenspan if she and her associates assessed BMI differences by ethnicity.
"We don’t have the power in our smaller cohort," she said. "We are looking at that in the larger 1,200 cohort."
The Relation Between Puberty and Breast Cancer
In addition to the San Francisco cohort, investigators are prospectively evaluating girls in Cincinnati and New York as part of the larger Breast Cancer and the Environment Research Program. This federally funded study is assessing the effect of early environmental exposures that could potentially trigger earlier pubertal development, and thus increase the risk of breast cancer. "We know that age of menarche is a risk for breast cancer," Dr. Greenspan said.
"There is growing evidence that timing of exposures may be important to determining breast cancer risk, and puberty may be an important window of susceptibility," Dr. Greenspan said.
The CYGNET study just entered year 6. Annual visits include a physical examination, evaluation of urine and blood samples, activity measurements, food recall, and questionnaires. One expert instructed all research staff to rate Tanner sexual maturity ratings.
Evaluation of tempo and menarche is a future goal for the CYGNET researchers. By the end of year 5, fewer than 20 girls have had menarche, Dr. Greenspan said.
"That is not enough yet to report. We are following the girls through at least year 10," so those data will be coming out, she added.
The Breast Cancer and the Environment Research Program is funded by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Greenspan said that she had no relevant financial disclosures.