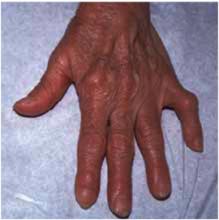
That same day, another patient was seen with painful hands (Figure 2). What type of arthritis does she have, and how does it differ from the condition of the patient in Figure 1 ?
FIGURE 2
Another patient with hand pain
The obvious ulnar deviation of her fingers and the swelling of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints (Figure 1) are strongly indicative of rheumatoid arthritis. The patient in Figure 2 has swelling and deformities in her proximal inter-phalangeal (PIP) and distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, indicating that she most likely has osteoarthritis. The swelling of the PIP joints is called Bouchard’s nodes; the swelling of the DIP joints is called Heberden’s nodes.
Differential diagnosis: types of arthritis
The first decision point in diagnosing chronic (>6 weeks) polyarticular joint pain is distinguishing between inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis. Key features of inflammatory arthritis are stiffness in the morning or after inactivity, and visible joint swelling. The differential diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis includes rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthropathies, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
After the age of 50, maturity-onset seronegative synovitis syndrome and crystal-induced synovitis should also be considered.1 Although osteoarthritis is considered noninflammatory, inflammation of the joint tissue occurs occasionally due to the joint’s degenerative loss of cartilage and bony overgrowth.