I would like to congratulate Tovar and colleagues (“LDL levels in diabetes: How low should they go?” J Fam Pract 2007; 56:634–640) on a bold article that brings some measure of rationality to this field.
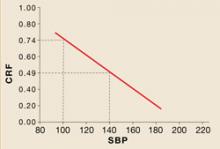
In my work, I have shown that it is the mix of the 3 main cardiovascular risk factors, not blood sugar levels per se, that is critical in determining the atherothrombotic disease (ATD) risk in patients with diabetes.1 The predictive/therapeutic tool that I use is a multifactorial graph (FIGURE) with the atherogenic/antiatherogenic balance of LDL and HDL cholesterol, expressed as the Cholesterol Retention Fraction (CRF, or [LDL-HDL]/LDL) placed on the ordinate of the graph and the systolic blood pressure (SBP) on the abscissa. The graph has a diagonal line, the threshold line, above which (in my practice) lie 85% of all my ATD patients.
Figure
A predictive tool for atherothrombotic disease
CRF: cholesterol retention fraction ([LDL-HDL]/LDL)
SBP: systolic blood pressure
A combination of a high CRF and high SBP— points above the red line—predict a higher risk of atherothrombotic events.
Of the 15% of ATD patients whose CRF-SBP plots lie below the threshold line, most are cigarette smokers, current or past. That leaves only 6% of my ATD patients who could not have been predicted by CRF-SBP plots above the threshold line and cigarette smoking status.
The graph predicts equally well in patients with normoglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, and diabetes. Using this graph, no treated patient of mine— diabetic or not—has had an acute trans-mural MI in the past 7 years.
Apropos the Tovar article, the answer to, “How low should the LDL level be?” should be, “It depends on how low the HDL level is.” The goal is to bring the CRF-SBP plot below the threshold line. If the HDL level is very low, then the CRF-SBP plot will be above the threshold line, even if the LDL level is <100 mg/dL. When this occurs, I refer to the data regarding LDL and plaque stabilization/regression referenced elsewhere.2
Any therapy that brings the LDL to 90–99 mg/dL results in plaque stabilization/regression in 80% of cases; bringing LDL to 80–89 mg/dL (stabilization/regression in 84% of cases); and bringing LDL to ≤79 mg/dL (stabilization/regression in 93% of cases). So, when HDL is very low, I aim for an LDL ≤79 mg/dL goal.
William E. Feeman, Jr, MD
The Bowling Green Study Center,
Bowling Green, Ohio; bgs43402@yahoo.com