Diagnosis hinges on these criteria
Two major criteria are required to make a diagnosis of Sweet’s syndrome. They are:2
- the abrupt onset of tender, erythematous plaques or nodules (FIGURE 2)
- a predominately neutrophilic infiltration in the dermis without leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
At least 2 of 4 minor criteria must also be present:2
- a precedent respiratory or gastrointestinal (GI) infection, vaccination, inflammatory disease, malignancy, or pregnancy
- malaise and fever
- elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and leukocytosis with a left shift. (Our patient’s erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 93 mm/h; her C-reactive protein was 11.47 mg/dL.)
- excellent response to corticosteroids or potassium iodide.
Although skin manifestations are a hallmark sign (which makes Sweet’s syndrome an important differential diagnosis for an unusual case of cellulitis, or one that is unresponsive to antibiotics), many possible coincident manifestations can occur. These include arthralgia, myalgia, headache, and malaise.5 Multi-system involvement has also been reported, affecting bone, the central nervous system, eyes, kidneys, heart, lungs, and GI tract.5
FIGURE 2
Another presentation of Sweet’s syndrome
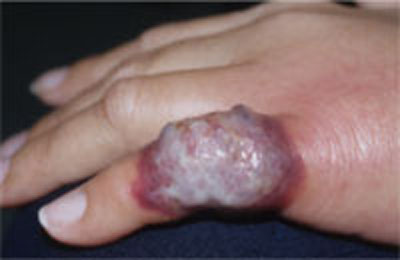
Some Sweet’s syndrome lesions appear "juicy." This lesion occurred at the site of minor trauma (pathergy) in a patient who was febrile and systemically ill.

