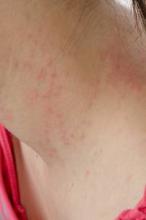
Contrary to conventional wisdom, atopic dermatitis persists well into the second decade of life and probably longer, based on data from a prospective longitudinal study published online April 3 in JAMA Dermatology.
At every age studied (2-26 years), more than 80% of patients reported having symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD) or taking AD medication in the past 6 months, reported Dr. David J. Margolis and his associates at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
"Past teaching that nearly 50%-70% of children with AD will achieve a resolution of their AD by age 12 years was not achieved in our study," the researchers said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 April 3 [doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2013.10271]).
The study enrolled 7,157 children aged 2-17 years who had physician-diagnosed mild to moderate AD. In a Kaplan-Meier survival estimate of 2,416 patients followed for at least 5 years, only by age 20 years did 50% of patients report at least 6 months free of AD symptoms or medications.
The findings are consistent with recent data suggesting that AD or eczema affects similar proportions of children and adults in the United States, the researchers said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and by Valeant Pharmaceuticals, maker of the atopic dermatitis drug pimecrolimus. The authors reported no individual conflicts of interest.