Data Analysis
Descriptive Summary of PCI Contributions
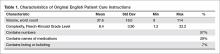
The 100 PCIs were summarized in terms of volume (word count), complexity (Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level index [13]), and content (medication names, references, formatting) (Table 1). Word count and grade level were calculated using Microsoft Word (Microsoft Corp, Redmond WA).
Safety Analysis
Concordance analysis. A safety translation concern as defined in this study (“might cause harm”) is very subjective. To reduce some of the variation in assessment of safety, we identified 4 members of the bilingual panel whose safety assessments of MBTE were most similar to the most concordant 4 monolingual raters’ assessment of MBTE safety. The goal was to select the bilingual panel of 4 that was most “typical” of the behavior of a “typical” monolingual individual with respect to assessing the safety of an individual MBTE translation. We then used this bilingual panel to identify 2 sets of “unsafe” machine Spanish and MBTE PCI translations: PCIs where ANY of the 4 bilingual raters identified a safety concern in machine Spanish or MBTE, and PCIs where MOST (at least 3) of the 4 bilingual raters agree that PCI translation was “unsafe”.
An expansion of Cohen’s kappa was used to identify the most concordant pairing of 4 bilingual panel members and 4 monolingual panel members [14]. All pairwise comparisons of monolingual and bilingual panel members were coded as follows: +1 was scored when 2 raters were concordant (both scored safe or unsafe) and –1 was scored for discordant pairs. For the 225 possible pairings of 4 panel members (15 combinations of 4 of 6 bilingual, 15 combinations of 4 of 6 monolingual raters), the 100 PCI items scores ranged from +16 (absolute agreement of the 2 panels of 4) to –16 (absolute discordance). For each pairing, we summed the scores for the 100 PCIs to determine the most concordant 4 monolingual and 4 bilingual raters (highest summed scores), which were then used for all subsequent analyses of safety and quality.
Original English characteristics of unsafe translation.
A logistic regression was performed with safety as the dependent variable (safe/unsafe defined by bilingual raters) with explanatory variables of word count, grade level, and reference to medication in OE.
Quality Assessment
Bilingual and monolingual raters assessments of translation quality. We assessed the correlation between the bilingual quality ratings of machine Spanish vs. MBTE and conducted paired t tests comparing mean bilingual machine Spanish and MBTE ratings. High correlation and absence of a significant difference in means would support the notion that MBTE could be used to reliably assess machine Spanish quality.
We also assessed the correlation between bilingual quality assessments of MS vs. monolingual raters’ assessments of MBTE, and conducted paired comparison t tests comparing bilingual machine Spanish and monolingual MBTE quality ratings. These analyses assess the ability of an English-only reader of MBTE to predict the quality of machine Spanish, as determined by a bilingual rater. High correlation and absence of a significant difference in means would support the notion that MBTE could be used by an English-only speaker to reliably assess machine Spanish quality.
Associations between original English content and translation quality. Objective measures of original English were correlated via stepwise linear regression with bilingual assessment of machine Spanish quality.
Results
PCI Contributions
Example PCIs were contributed by 88 individuals and are summarized in Table 1. The 100 original English PCIs and the machine Spanish and MBTE translations obtained via Google Translate are available from the authors upon request.
Safety
Concordance Analysis
The 6 monolingual and bilingual raters agreed on the safety of 73 MBTE PCIs. The most concordant pairings of 4 agreed on 81 items. The least and most concordant pairings had concordance values of 0.68 and 0.84, respectively. Subsequent analyses include data from only the 4 most concordant monolingual and bilingual raters.
Bilingual and Monolingual Safety Ratings
Both bilingual and monolingual raters assessed MBTE. On average, bilingual ratings of MBTE of safety were higher (0.987) than monolingual ratings (0.925) (t = –3.897, P = 0.0002).
Identification of Unsafe Translations in Machine Spanish and MBTE
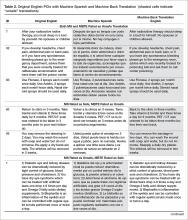
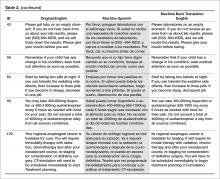
The bilingual panel identified 11 translations (either machine Spanish or MBTE) as unsafe: MS translation was unsafe for 9 items, MBTE unsafe for 5 items, with some items identified as unsafe in terms of both machine Spanish and MBTE. The original English, machine Spanish, and MBTE for these PCIs are listed in Table 2. One item (#93) revealed a machine Spanish drug dosing ambiguity that was not present in the MBTE, with safety concern expressed by 3 of 4 bilingual raters.
Original English characteristics of Unsafe Translation
A stepwise logistic regression was performed to evaluate whether characteristics of the original English text predicted the PCI being judged as having a safe or unsafe machine Spanish translation. The explanatory variables (listed in Table 1) evaluated were word count, reading grade level, inclusion of reference to a specific medication, inclusion of numbers (as in "take 2 tablets"), and inclusion of numbered statements (as in "1. Call if your cough worsens"). The stepwise selection procedure dropped number references and numbered sentences, although post hoc analysis showed that number references and medication references occurred so commonly together that they were essentially interchangeable. The final regression model included word count, reading grade level, and medication reference. The significant factors of reading grade level and medication reference had odds ratio (95% confidence interval) of 1.12 (1.01 to 1.41) and 4.91 (1.07 to 22.7) respectively (P = 0.042 each). As reading grade level includes word count per sentence and syllable count per word as linear predictors, the inclusion of word count in the model is likely to increase the discrimination of complex words of many syllables in predicting the occurrence of unsafe machine Spanish.