In a bicornuate uterus, the fundus is indented and the vagina is normal. This anomaly occurs when the müllerian ducts fuse only partially. The result is varying degrees of separation of the uterine horns.
Pregnancy outcomes appear to be similar to those of the general population. However, some women develop early pregnancy loss, preterm labor, incompetent cervix, or malpresentation.
Treatment is open surgical reunification.
CASE 4 Embryonic rest cells
A 55-year-old woman complains of “fullness” in the vagina, especially during intercourse. Upon examination, a 4- to 5-cm fluid-filled cyst is visible at the right posterior fornix.
What type of cyst is it?
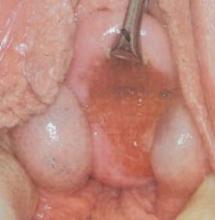
Gartner’s duct cysts from embryonic rest cells arise from remnants of the metanephric duct system. They usually develop on the lateral vaginal walls or fornix (FIGURE 7), unlike epidermal inclusion cysts, which are generally located on the posterior wall or at the cervical–vesical junction. Although they sometimes cause dyspareunia or make it difficult for the patient to insert a tampon, they are usually asymptomatic unless they are large. Intervention is not indicated unless the patient is symptomatic.
Treatment. Marsupialization rather than excision is the treatment of choice because these embryonic rest cells may extend deep into the retroperitoneum.
FIGURE 7 Gartner’s duct cysts
These bilateral cysts developed from embryonic rest cells.