Hereditary coproporphyria
The team considered hepatic porphyias because of new-onset symptoms of mood lability, confusion, orthostasis, unsteady gait, weakness, dermatologic conditions on hands not responsive to treatment, and general malaise. Mr. J was diagnosed with HCP, a type of porphyria caused by a defect in coproporphyrinogen oxidase that leads to an accumulation of coproporphyrinogen III. This precursor, as are many porphyrin precursors, is neurotoxic, leading to neurovisceral or neuropsychiatric effects. Although in Mr. J’s case the coproporphyrinogen III value from the 24-hour drug screen was only modestly elevated, it has been noted that levels of excreted prophyrins do not necessarily correlate with symptom severity.3
In the past, porphyria testing was performed using the Watson-Schwartz test, which used Ehrlich’s reagent to precipitate porphyrins in a urine sample,4 and was used as a “bedside” test. Interestingly, porphyrins—not the iron found in the heme molecule—are precipitated in this test and cause the reddish-purple coloration of the urine sample. When quantitative testing was developed, a 24-hour sample of urine—kept on ice and away from ambient light, later to be frozen when sent to the laboratory—became the standard tool for testing for porphyrins. Now DNA testing can be used to diagnose HCP.
OUTCOME Symptoms resolve
Mr. J is started on loxapine, 20 mg at bedtime, and his symptoms resolve within 2 weeks. He maintains some baseline delusional ideation consistent with his history of schizoaffective disorder, but he is more social, his personal hygiene improves, he attends groups, eats in the cafeteria with his peers, and is no longer confused.
The author’s observations
In the 1950s, chlorpromazine was used to treat AIP.5 Mr. J received loxapine, a mid-potency first-generation antipsychotic, although it has been this author’s observation that high-potency first-generation antipsychotics are not effective for treating porphyria.
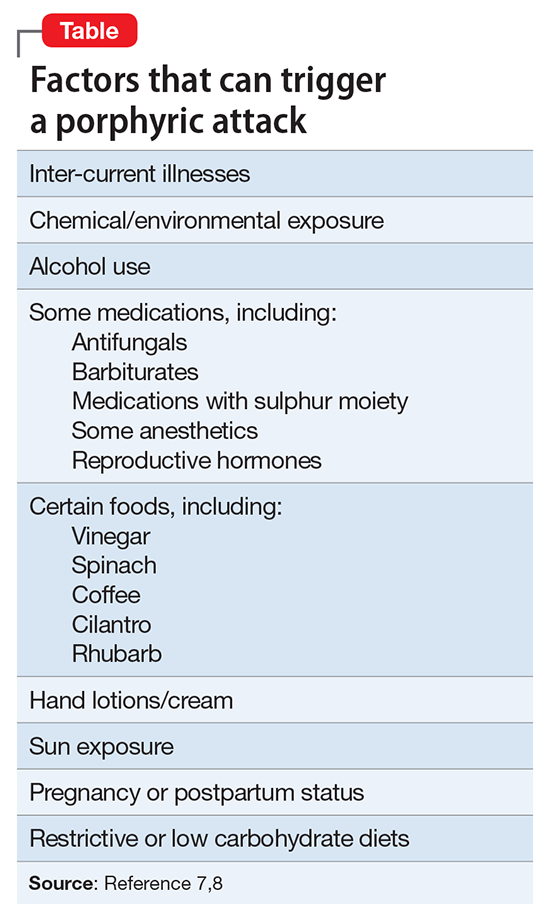
Other treatment modalities include phlebotomy, and more extreme treatments include liver transplantation for hepatic porphyrias or bone marrow transplantation for erythropoietic porphyrias. PCT can be treated with scheduled phlebotomy and/or medication. The mechanism by which treatment (whether dietary or avoidance of triggers) is thought to be based on negative feedback to a rate limiting step in the heme synthesis chain (∆amino levulinic acid). Method of action (and this author’s observations with loxapine) is thought to be effective in part due to peripheral and neuromuscular blocking action.6Another mainstay of porphyria treatment is avoiding triggers (Table).7,8 It is unclear what could have triggered the development of HCP in Mr. J. It may be that this was genetic, but because of incomplete dominant inheritance, it is unknown but can be assumed. There was a large scale occurrence of iatrogenic porphyria (PCT) in Turkey3 due to exposure to hexachlorobenzene in the wheat supply. Porphyrias usually are passed down in families. Due to incomplete penetrance of inheritance, many with an enzyme defect will not become symptomatic. Usually symptoms present post-puberty, and often, but not always, in the fourth decade of life. It is unknown when a potential trigger will cause the illness.