Case Report
A 26-year-old woman with a medical history of newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus (DM), obesity, and asthma was evaluated as a hospital consultation with a vegetative plaque on the left lateral ankle of 13 months’ duration. The lesion first appeared as a red scaly rash that became purulent. The lesion had been treated with multiple rounds of topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics, topical antifungals, and corticosteroids without resolution. The patient denied pain or any decrease in ankle mobility. Review of systems was otherwise negative.
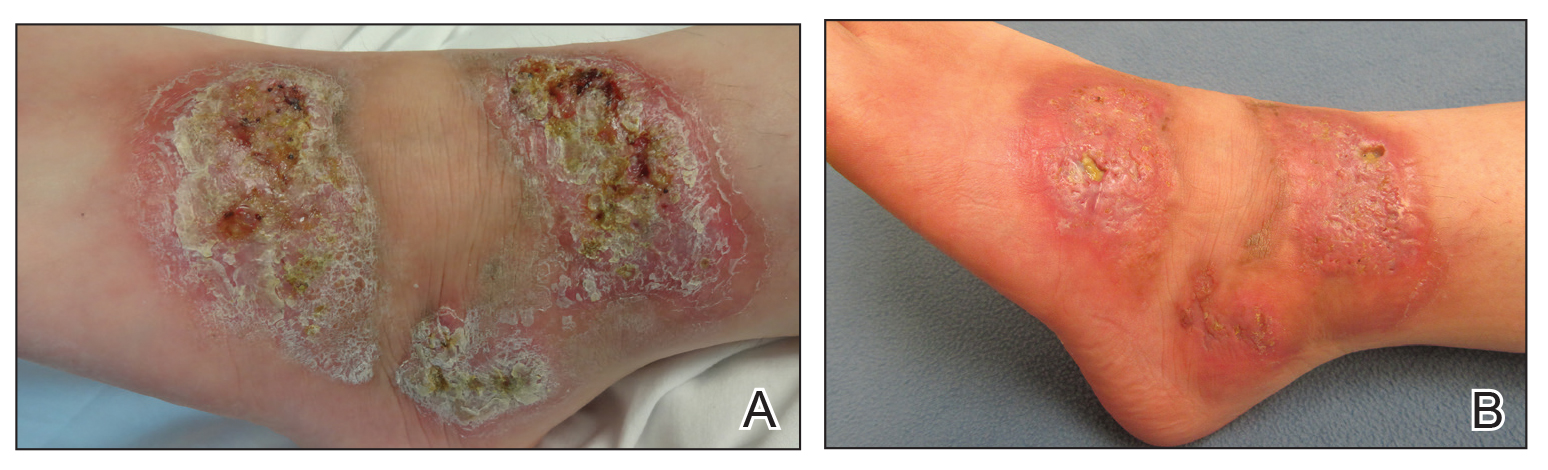
On physical examination, 3 large, pink, scaly, crusted plaques with surrounding erythema were observed (Figure 1A). On palpation, purulent drainage with a foul odor was noted in the area underlying the lesion. Initial punch biopsy demonstrated epidermal hyperplasia with neutrophil-rich sinus tracts consistent with pyoderma vegetans (PV)(Figure 2A). Tissue culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus anginosus. Cultures for both fungi and acid-fast bacilli were negative for growth.
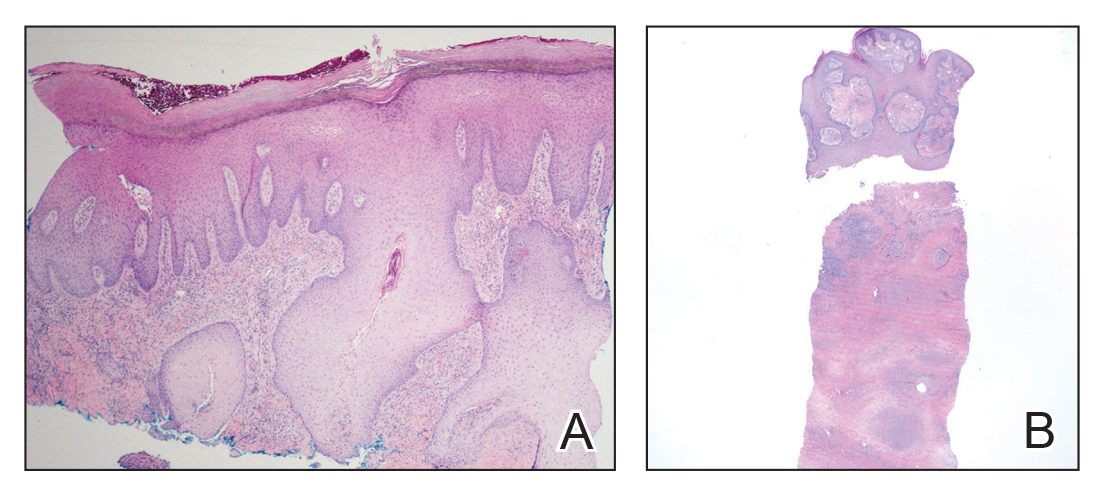
Figure 2. A, First punch biopsy of purulent crusted lesion on the left foot revealed epidermal hyperplasia with neutrophilrich sinus tracts (H&E, original magnification ×4). B, Second deeper punch biopsy of a crusted lesion on the left foot revealed a layered granulomatous infiltrate with sclerosis throughout the dermis (H&E, original magnification ×2).
The patient was treated with mupirocin ointment 2% and 3 months of cephalexin 250 mg twice daily, which cleared the purulent crust; however, serous drainage, ulceration, and erythema persisted. The patient needed an extended course of antibiotics, which had not been previously administered to clear the purulence. During this treatment regimen, the patient’s DM remained uncontrolled.
A second deeper punch biopsy revealed a layered granulomatous infiltrate with sclerosis throughout the dermis most consistent with necrobiosis lipoidica (NL)(Figure 2B). Direct immunofluorescence biopsy was negative. Once the PV was clear, betamethasone dipropionate ointment 0.05% was initiated to address the residual lesions (Figure 1B).
Physical examination combined with histopathologic findings and staphylococcal- and streptococcal-positive tissue cultures supported a diagnosis of NL with superimposed PV.
Comment
Necrobiosis lipoidica is a chronic granulomatous disease characterized by collagen degeneration, granulomatous formation, and endothelial wall thickening.1 The condition is most commonly seen in association with insulin-dependent DM, though it also has been described in other inflammatory conditions. A case of NL in monozygotic twins has been reported, suggesting a genetic component in nondiabetic patients with NL.2 Necrobiosis lipoidica affects females more often than males.
The pathogenesis of NL is not well understood but likely involves secondary microangiopathy because of glycoprotein deposition in vessel walls, leading to vascular thickening. Histopathology reveals palisading and necrobiotic granulomas comprising large confluent areas of necrobiosis throughout the dermis, giving a layered appearance.3