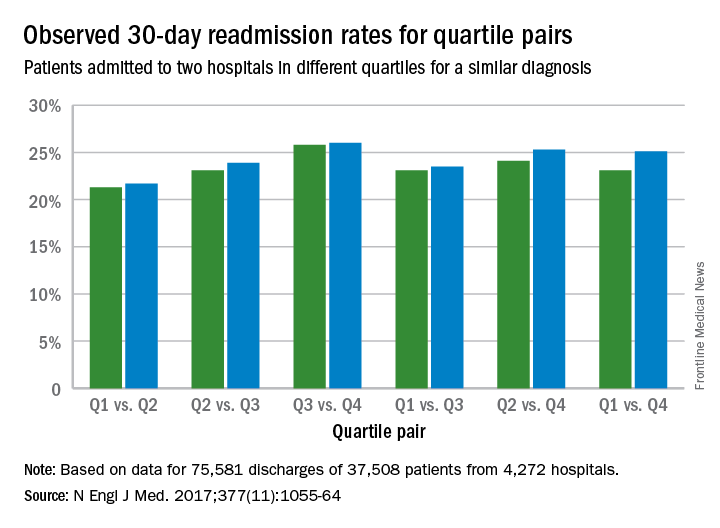
Poorer-performing hospitals have higher readmission rates than better-performing hospitals for patients with similar diagnoses, a study shows.
Lead author Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and his colleagues analyzed Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services hospital-wide readmission data and divided data from July 2014 through June 2015 into two random samples. Researchers used the first sample to calculate the risk-standardized readmission rate within 30 days for each hospital and classified hospitals into performance quartiles, with a lower readmission rate indicating better performance. The second study sample included patients who had two admissions for similar diagnoses at different hospitals that occurred more than 1 month and less than 1 year apart. Researchers compared the observed readmission rates among patients who had been admitted to hospitals in different performance quartiles. The analysis included all discharges occurring from July 1, 2014, through June 30, 2015, from short-term acute care or critical access hospitals in the United States involving Medicare patients who were aged 65 years or older.
In the period studied, there were a total of 7,163,152 hospitalizations, of which 6,910,341 met the inclusion criteria for the hospital-wide risk-standardized readmission measure. Of these hospitalizations, 3,455,171 discharges (involving 2,741,289 patients and 4,738 hospitals) were randomly selected for the first sample for calculation of hospital-readmission performance. The second sample included 3,455,170 discharges, 132,283 of which involved patients who had two or more admissions for similar diagnoses at least 30 days apart.Results found that among the patients hospitalized more than once for similar diagnoses at different hospitals, the readmission rate was significantly higher among patients admitted to the worst-performing quartile of hospitals than among those admitted to the best-performing quartile (absolute difference in readmission rate, 2.0 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, 0.4-3.5; P = .001) (N Engl J Med. 2017. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1702321). The differences in the comparisons of the other quartiles were smaller and not significant, according to the study.
The findings suggest that hospital quality contributes at least in part to readmission rates, independent of patient factors, study authors concluded.
“This study addresses a persistent concern that national readmission measures may reflect differences in unmeasured factors rather than in hospital performance,” study authors noted in the study. “The findings suggest that hospital quality contributes at least in part to readmission rates, independent of patient factors. By studying patients who were admitted twice within 1 year with similar diagnoses to different hospitals, this study design was able to isolate hospital signals of performance while minimizing differences among the patients. In these cases, because the same patients had similar admissions at two hospitals, the characteristics of the patients, including their level of social disadvantage, level of education, or degree of underlying illness, were broadly the same. The alignment of the differences that we observed with the results of the CMS hospital-wide readmission measure also adds to evidence that the readmission measure classifies true differences in performance.”
Dr. Krumholz and seven coauthors reported receiving support from contracts with the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services to develop and reevaluate performance measures that are used for public reporting.
On Twitter @legal_med