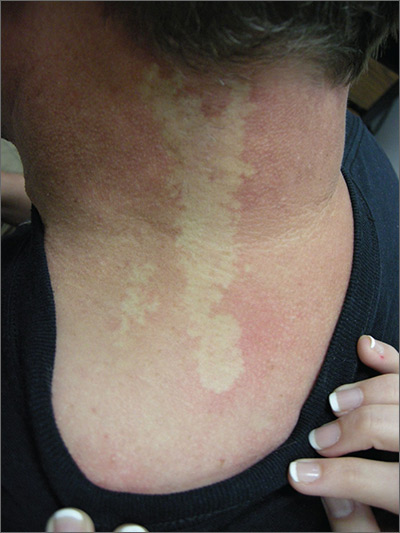
The FP diagnosed nevus anemicus in this patient.
Nevus anemicus is a congenital hypopigmented macule or patch that is stable in relative size and distribution. It occurs as a result of localized hypersensitivity to catecholamines and not as a result of a decrease in melanocytes. The localized hypersensitivity to catecholamines causes the affected area to stay lighter than the surrounding skin. On diascopy (pressure with a glass slide), the skin is indistinguishable from the surrounding skin.
There is no treatment for this benign condition, and it is not associated with any underlying malignancy or other health problem.
Photo courtesy of the University of Texas Health, San Antonio and text courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Smith M, Usatine R. Benign nevi. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, Chumley H. Color Atlas of Family Medicine . 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:945-952.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine , see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.