Stress fractures and stress reactions (early evidence of bone edema seen on MRI, indicating progression to stress fracture) of the proximal fifth metatarsal should be managed with strict activity modifications and a NWB short leg cast for 6 to 8 weeks, given the high risk of nonunion.
Midfoot fractures: The cuboid, cuneiforms, and navicular bone
Although fractures are less common in the midfoot, the midfoot serves an important role in weight bearing and stabilization. In addition, along with the metatarsal bones, the midfoot is critical to proper alignment and articulation.
Cuboid and cuneiform fractures
Cuboid fractures may occur with high-velocity trauma, foot inversion with external rotation of the tibia, a direct blow, or axial load on a plantar-flexed heel. Pain with weight bearing or with walking on toes is usually present. Cuneiform fractures are less common and rarely occur in isolation.6 Mechanisms of injury for cuneiform fractures include direct impact, axial loading on a dorsiflexed or plantar-flexed foot with rotational force, and severe rotation of the midfoot section in a fixed foot. Pain is usually localized to the dorsal or dorsomedial aspect of the foot.
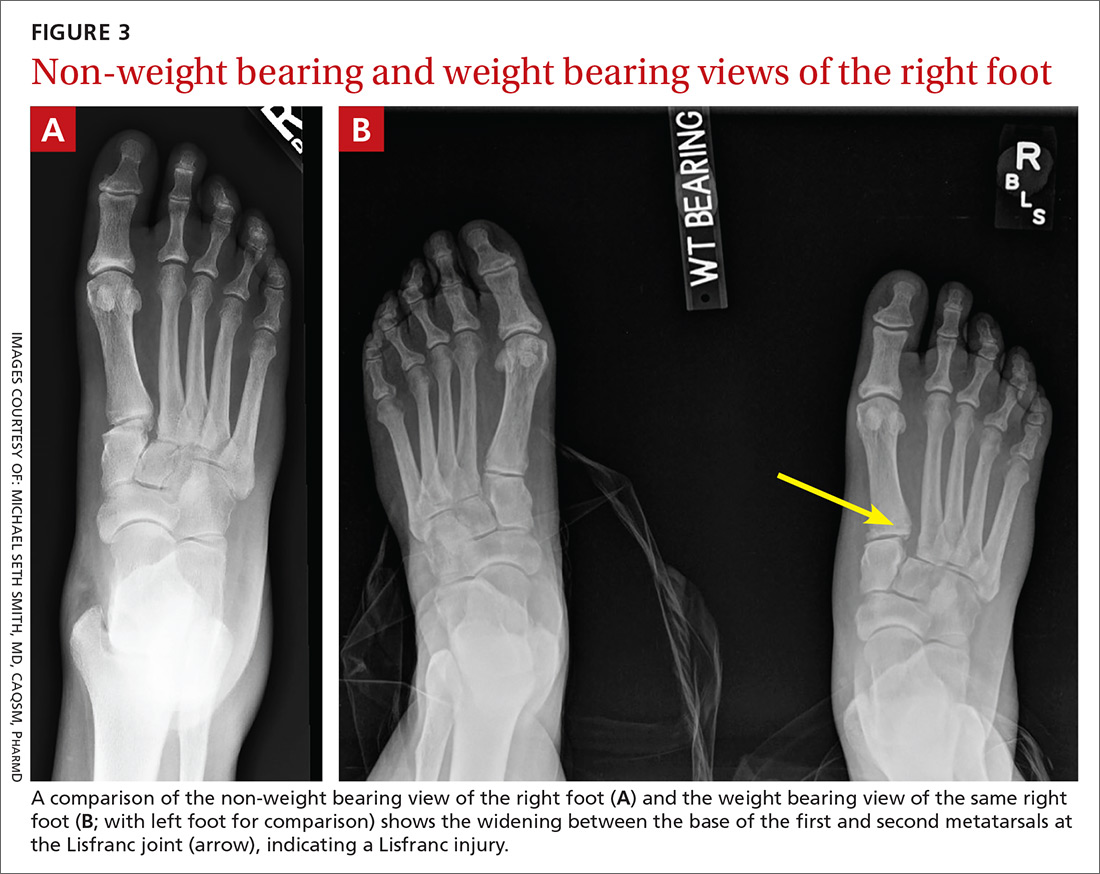
With these 2 midfoot injuries, the exam should include palpation of the cuboid, navicular, and cuneiform bones and careful inspection of the Lisfranc joint, as this can be injured in midfoot fractures.7 Obtain AP, lateral, and oblique views of the foot,5 and strongly consider bilateral weight-bearing films to evaluate for tarsometatarsal (TMT) joint complex injuries (typically Lisfranc joint complex injuries), given their association with midfoot fractures1 (FIGURE 3).
If the fracture is at or near the TMT joint complex, obtain a CT scan or MRI regardless of plain film findings to evaluate the Lisfranc joint complex. Because the Lisfranc joint is particularly important in midfoot stability, untreated injuries can lead to impaired gait or chronic foot pain and deformity. Early identification and surgical referral for these injuries is crucial.
Continue to: Navicular fractures