EVIDENCE SUMMARY
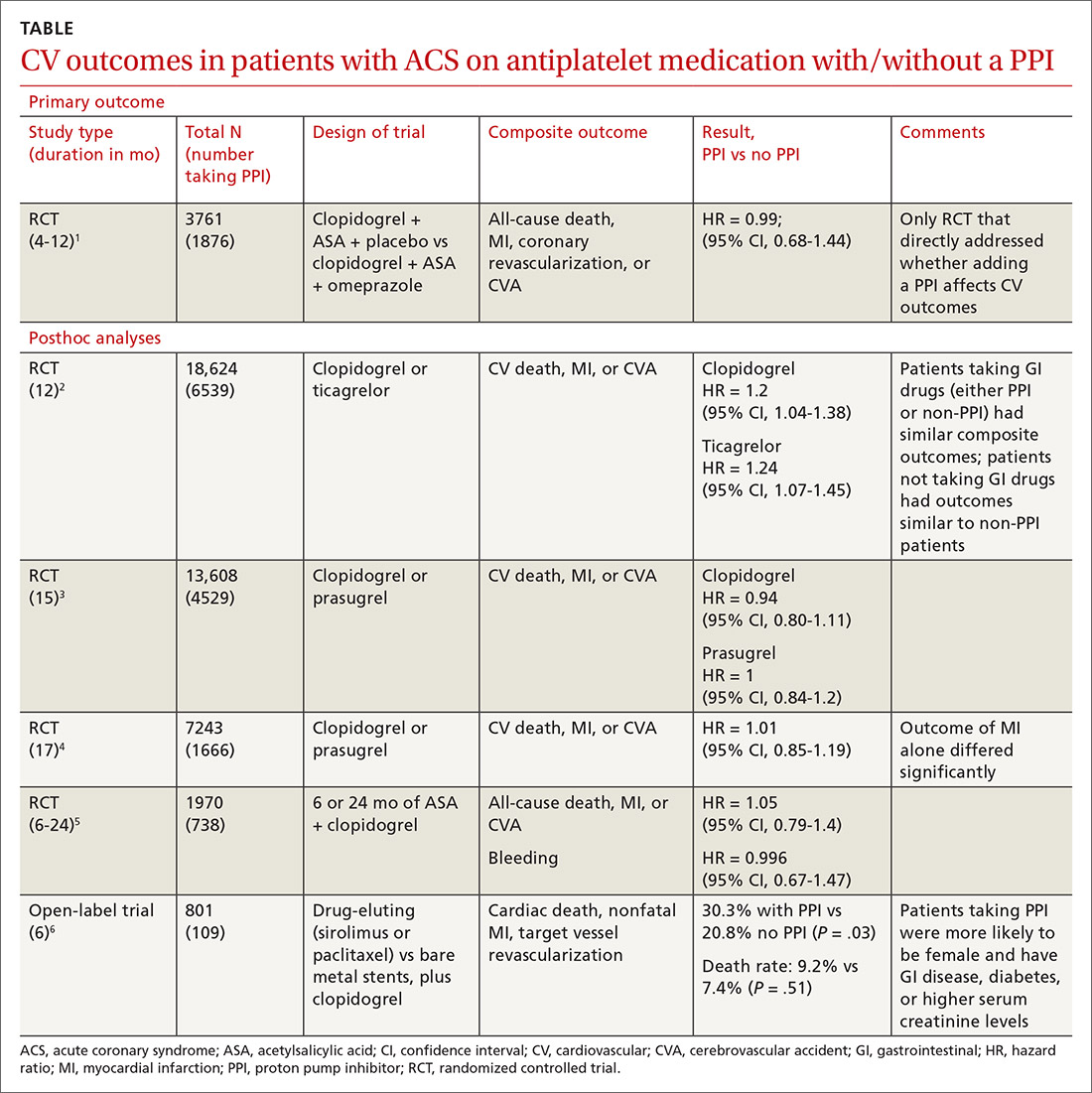
A double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled RCT comparing a combination of clopidogrel, aspirin, and omeprazole with clopidogrel, aspirin, and placebo found no increase in composite CV outcomes with the PPI (TABLE).1 Using a PPI did, however, significantly reduce gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03-0.56).Although several meta-analyses have been conducted, they all rely on this single RCT that directly addresses the question, plus post-hoc analyses of other RCTs.
Four of 5 analyses find little or no difference in CV outcomes with a PPI
Four of 5 posthoc analyses (which weren’t themselves randomized) of RCTs found unclear or no differences in composite CV outcomes with concurrent use of a PPI and antiplatelet therapy, after multivariate adjustment for differences in populations taking or not taking a PPI.
Posthoc analysis of the largest study found worse CV outcomes for both clopidogrel and ticagrelor with concomitant PPI use.2 However, patients on any GI drugs (PPI or non-PPI) had composite outcomes similar to patients on a PPI (PPI vs non-PPI GI treatment: HR = 0.98; 95% CI, 0.79-1.23), and patients not taking GI drugs had fewer composite outcomes compared with patients on a PPI (clopidogrel vs no GI therapy: HR = 1.29; 95% CI, 1.12-1.49; ticagrelor vs no GI therapy: HR = 1.30; 95% CI, 1.14-1.49). Researchers postulated that because the rate of composite outcomes increased equally for patients on any GI drug, the higher rate of CV adverse events with a PPI might have been related to GI disease rather than PPI use.
A similar posthoc analysis found no differences with or without PPI use among patients with ACS undergoing planned percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and assigned to clopidogrel or prasugrel.3 Researchers performed multivariate adjustment for differences in age, gender, ethnicity, and initial presence of unstable angina/non-ST-elevation MI.
A smaller study also found no significant differences in composite CV outcomes in patients using PPIs.4 Patients did have higher rates of MI (HR = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.91), but they were more likely to be older and have a previous diagnosis of non-ST-elevation MI, higher incidence of previous coronary artery bypass graft surgery, and history of peptic ulcer disease.
The fourth posthoc analysis of an RCT found that concomitant PPI use (91% of patients on lansoprazole) didn’t alter outcomes among patients undergoing PCI and receiving dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin.5 Researchers used a multivariate adjustment for differences in age, gender, and renal function and found no difference in outcomes during the 6-month or 24-month period. PPI prescription was at physician discretion. Researchers didn’t assess for dose-dependent effects of PPI.
A fifth, flawed study finds more adverse events with PPIs
A posthoc analysis of a smaller, open-label trial found increased major adverse cardiac events with PPI use among patients taking clopidogrel after PCI.6 Researchers didn’t adjust for differences in populations at baseline, however, and patients taking PPIs were more likely to be female or older and have diabetes, GI disease, or higher serum creatinine levels.
Continue to: Editor's takeaway