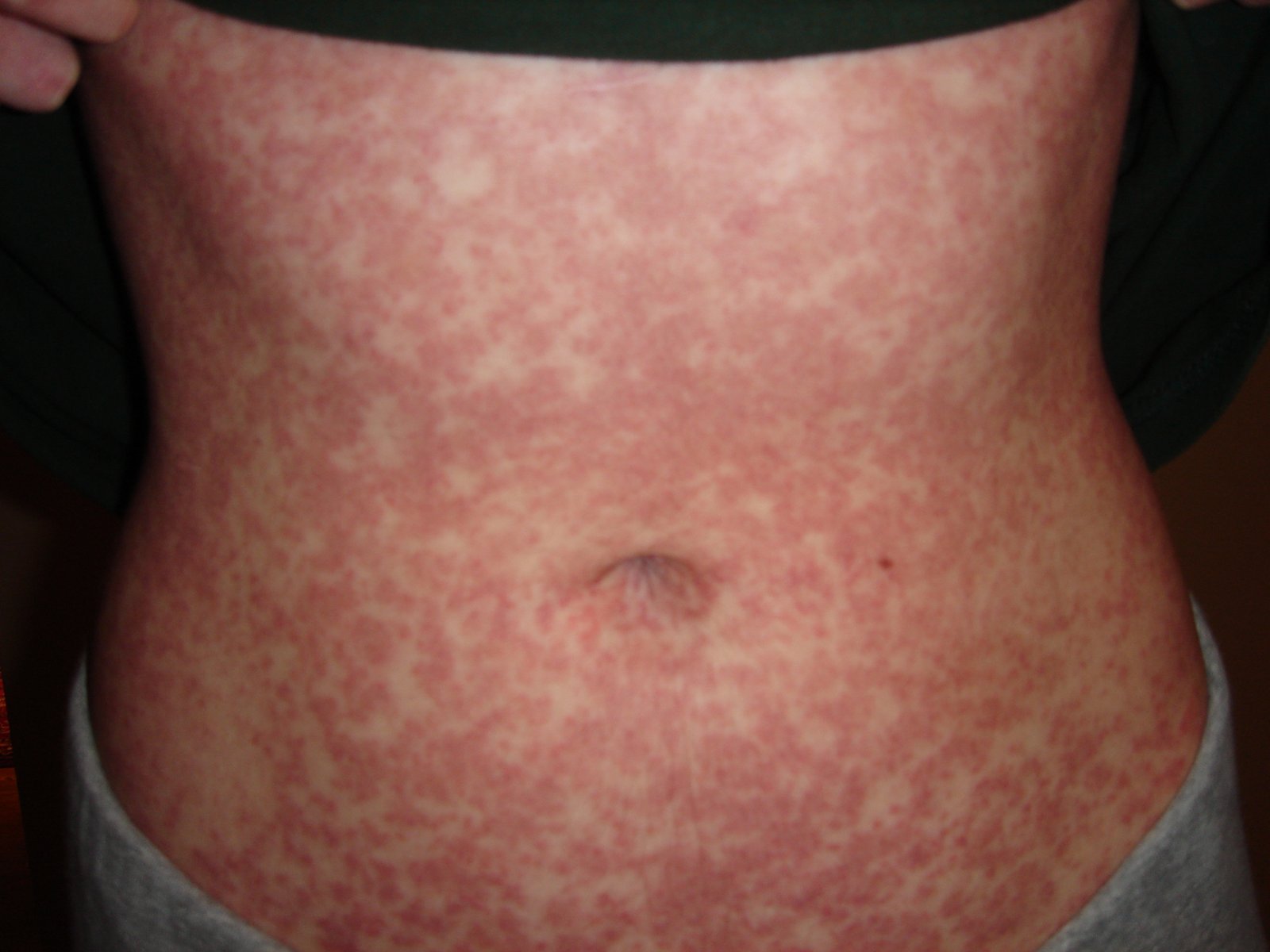
The FP suspected mononucleosis and sent the patient for a monospot test, which was positive. This morbilliform rash (like measles) is typical of an amoxicillin drug eruption in a patient with mononucleosis. The amoxicillin was stopped, and diphenhydramine was used for the itching. This is a typical maculopapular drug eruption. Mild desquamation is normal as the eruption resolves. This patient’s exanthem cleared within 5 days of stopping the amoxicillin; there was some slight desquamation on the hands.
It remains unclear if this reaction was a transient immunostimulation or a true drug allergy. For safety purposes, it would be best to avoid giving this patient amoxicillin or ampicillin in the future. It’s possible that the patient may be able to take penicillin or a cephalosporin safely in the future. A referral to an allergist might help to sort out this issue.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Allred A, Usatine R. Cutaneous drug reactions. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. The Color Atlas of Family Medicine. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2009:869-877.
To learn more about The Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see:
• http://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Family-Medicine/dp/0071474641
You can now get The Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app for mobile devices including the iPhone and iPad by clicking this link: