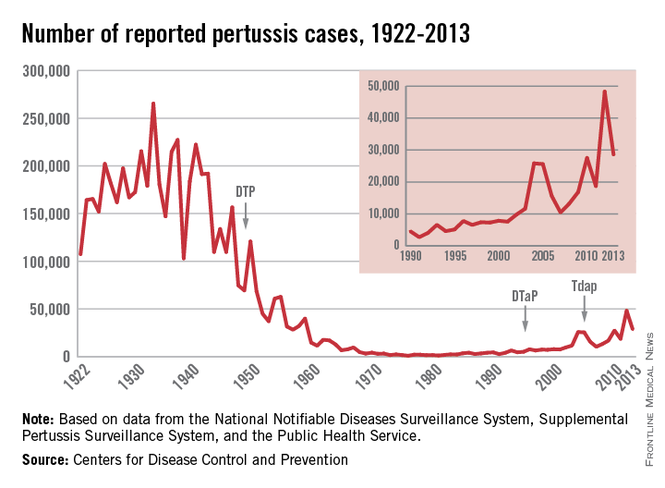
There were more than 48,000 cases of pertussis in the United States in 2012, the highest number since 1955, the CDC reported.
After a low of 1,010 cases in 1976, the annual number of pertussis cases grew slowly through the 1980s and 1990s, with 2002 being the last year there were fewer than 10,000 reported pertussis cases. The number of cases dropped in 2013, although the 28,639 cases was the second highest since 1959. There were 20 pertussis deaths in 2012 and 9 in 2013, the CDC data show.
The highest rate of infection is in children aged less than 6 months: 126.7/100,000 in 2012.That year, children aged 7-10 years had the second highest rate at 58.5/100,000, with children aged 11-19 years at 38/100,000, and children aged 1-6 years at 34.1/100,000, according to the CDC. Overall U.S. incidence was 15.4/100,000.
Things improved some in 2013. Children aged less than 6 months still had the highest rate of infection at 138/100,000. Children aged 7-10 years had the second highest rate at 26.2/100,000, followed by children aged 1-6 years at 18.8/100,000, and children aged 11-19 years at 17.6/100,00. Overall U.S. incidence was 7.69/100,000.
The CDC data were collected by the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System and the Supplemental Pertussis Surveillance System.